Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
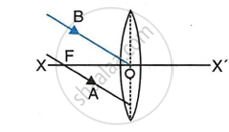
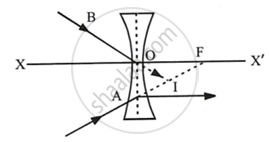
In the diagram below, XX’ represents the principal axis, O the optical centre and F the focus of the lens. Complete the path of rays A and B as they emerge out of the lens.
 |
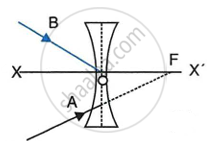 |
| (a) | (b) |
Solution
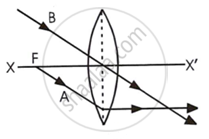
The path of rays A and B as they emerge out of the lens is shown.
 |
 |
| (a) | (b) |
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What is a lens?
Explain optical centre of a lens with the help of proper diagram(s).
Study the diagram shown in Fig. 5.56
where is the object located?
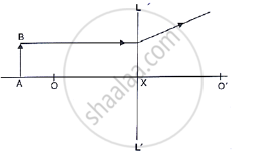
In the following diagram , the object and the image formed by the respective lenses are shown. Complete the ray diagram, and locate the focus. Find the focal length of the lens.

Fig. shows two rays of light Op and OQ coming from an object at the bottom of a pond, incident on the water surface.
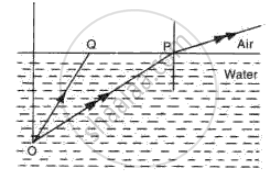
(a) Mark on the diagram
(i) The angle of incidence of ray OP,
(ii) The angle of refraction of ray Op,
(iii) The position of image of the object as seen from above.
(iv) An approximate path of the ray OQ.
(b) Explain, why do the rays of light change directions on passing from water to air.
(c) A fish in water sees everything outside the water by rays of light entering its eye in a small cone of light. Draw a diagram and explain how does this happen.
Name the subjective property of light related to its wavelength.
State the nature and position of the object on the principal axis to obtain a real and magnified image.
Complete the following diagram and state what happens to the ray of light after refraction through the lens.
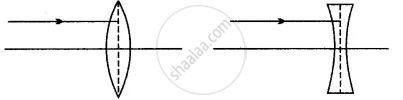
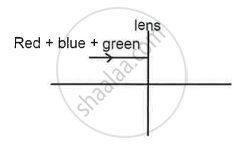
Mixture of red + blue + green is passed through a convex lens as shown in the diagram below. State whether the ray passes through a single point or through different points on the principal axis after refraction.