Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
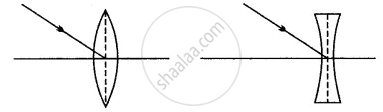
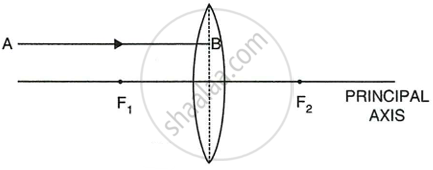
Complete the following diagram and state what happens to the ray of light after refraction through the lens.
Solution
A ray of light parallel to the principal axis, after refraction by the lens, either passes through its principal focus or appear to pass through its principal focus.
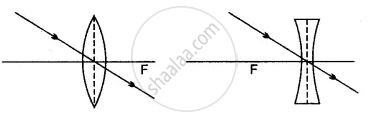
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
In the following figure (a) and (b), F1 and F2 are positions of the two foci of thin lenses. Draw the path taken by the light ray AB after it emerges from each lens.
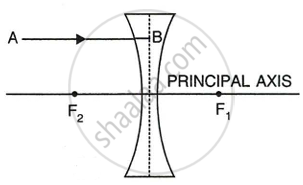 |
| (a) |
 |
| (b) |
A ray of light after refraction through a lens emerges parallel to the principal axis of the lens. The incident ray either passes through ______.
A ray of light incident on a lens parallel to its principal axis, after refraction passes through or appears to come from ______.
Study the diagram shown in the following Figure.
Name the lens LL’ and draw its outline.
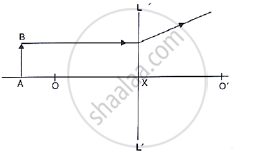
State the condition of the following:
A lens has both its focal lengths equal.
State the condition of the following:
A ray passes undeviated through the lens.
(a) Draw a sketch to show how a lens is able to produce an image of the sun on a paper screen.
(b)(i) Would you regard the rays from the sun as being divergent, parallel or convergent?
(ii) What is the name given to the point where such rays meet after they have passed through the lens?
(iii) How does the image of the sun sometimes burn a paper screen?
When does a ray of light falling on a lens pass through it undeviated?
Complete the following diagram and state what happens to the ray of light after refraction through the lens.