Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
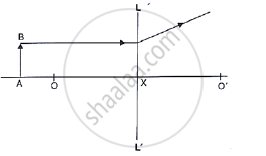
Complete the following diagram and state what happens to the ray of light after refraction through the lens.
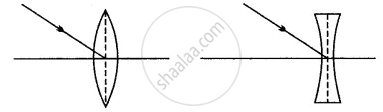
Solution
A ray of light goes undeviated through the optical centre of a lens, whether convex or concave.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What is a lens?
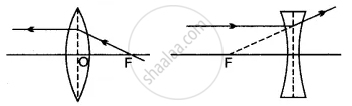
In figure, (a) and (b), F1 and F2 are the two foci of thin lenses and AB is the incident ray. Complete the diagram to show the path of the ray AB after refraction through each lens.
 |
| (a) |
 |
| (b) |
A ray of light after refraction through a lens emerges parallel to the principal axis of the lens. The incident ray either passes through ______.
Study the diagram shown in Fig. 5.56
what are the two other characteristics of the image?
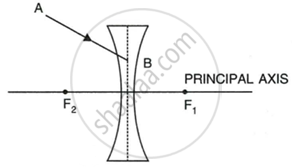
The diagram given below shows the position of an object OA in relation to a converging lens L whose foci are at F1 and F2.
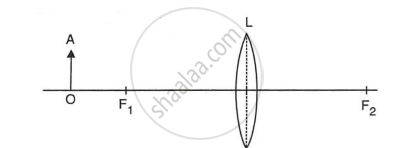
- Draw two rays to locate the position of the image.
- State the position of the image with reference to the lens.
- Describe three characteristics of the image.
- Describe how the distance of the image from the lens and its size change as the object is moved towards F1.
What type of lenses are used in spectacles worn by an old lady for knitting?
Define the term 'focus' of a lens.
Name the subjective property of light related to its wavelength.
Draw a ray diagram to show the image formed by a convex lens when the object is placed between F and 2F.
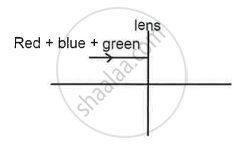
Mixture of red + blue + green is passed through a convex lens as shown in the diagram below. State whether the ray passes through a single point or through different points on the principal axis after refraction.