Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Define the term 'focus' of a lens.
Solution
Principal focus: Rays of light can pass through the lens in any direction and hence there will be two principal foci on either side of the lens and they are referred to as the first principal focus and the second principal focus of a lens.
First Principal Focus (F1)
It is a point on the principal axis of the lens such that the rays of light starting from it (convex lens) or appearing to meet at the point (concave lens) after refraction from the two surfaces of the lens become parallel to the principal axis of the lens.
Second Principal Focus (F2)
It is a point on the principal axis of the lens such that the rays of light parallel to the principal axis of the lens after refraction from both the surfaces of the lens pass through this point (convex lens) or appear to be coming from this point.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
In figure, (a) and (b), F1 and F2 are the two foci of thin lenses and AB is the incident ray. Complete the diagram to show the path of the ray AB after refraction through each lens.
 |
| (a) |
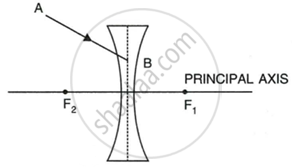 |
| (b) |
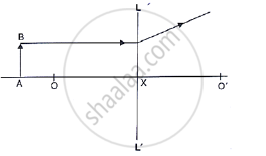
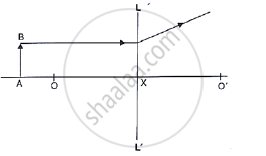
In the diagram below, XX’ represents the principal axis, O the optical centre and F the focus of the lens. Complete the path of rays A and B as they emerge out of the lens.
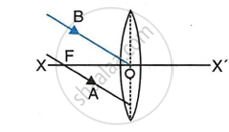 |
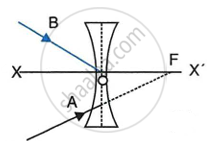 |
| (a) | (b) |
Study the diagram shown in the following Figure.
Name the lens LL’ and draw its outline.
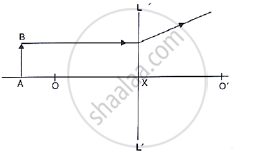
Study the diagram shown in Fig. 5.56
Where is the image formed?
Study the diagram shown in Fig. 5.56
what are the two other characteristics of the image?
(a)A ray of light is incident at 45° on the face of
(i) A rectangular block of glass.
(ii) A 600 glass prism.
(b) Draw a sketch showing how the ray of monochromatic ray of light passes through glass in each case.
(c) With the aid of a diagram, explain how the face of a right angled prism may totally reflect incident on it.
(d) A thick plane mirror produces several faint images in addition to a prominent one. Draw a ray diagram showing how reflection and refraction produce all these images.
(e) Fig. represents a stone S at the bottom of a pond of water. Using the two rays, as shown, complete the ray diagram to show where the image of the stone appears when viewed from E.

(f) What is a''mirage'? Explain with the help of a diagram.
(g) A man observes the bottom of a swimming pool of 3 m depth. If the refractive index of water is 1.3, what is the apparent depth of water?
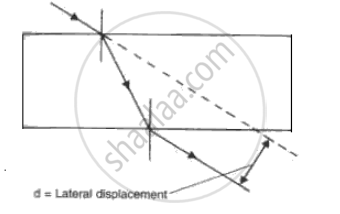
(h) When a ray of light undergoes refraction through a glass slab and when it emerges it is displaced laterally (Fig). What are the factors on which the lateral displacement depends?
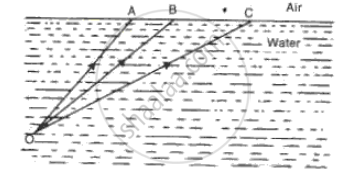
(i) Fig. shows three rays of light OA, OB and OC passing from water to air, making angles 490, 410 and 350 with the horizontal surface respectively. Draw an approximate path of the emergent ray for each. (Critical angle of water is 490.)
How will you differentiate between a convex and a concave lens by looking at a distant object.
State the nature and position of the object on the principal axis to obtain a real and magnified image.
