Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The diagram given below shows the position of an object OA in relation to a converging lens L whose foci are at F1 and F2.
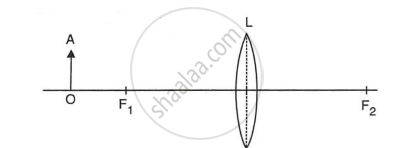
- Draw two rays to locate the position of the image.
- State the position of the image with reference to the lens.
- Describe three characteristics of the image.
- Describe how the distance of the image from the lens and its size change as the object is moved towards F1.
Solution
- The position of image A1B1 is located.
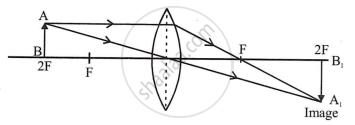
- The image is formed beyond 2F2 on the other side of the lens.
- Image is real inverted, beyond 2f and enlarged.
- Size of image increases and distance of image from the lens increases.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
State the condition when a lens is called an equi-convex or equi-concave.
Distinguish between a real and a virtual image.
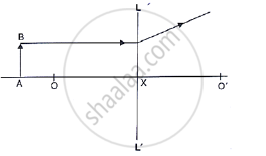
Study the diagram shown in Fig. 5.56
Where is the image formed?
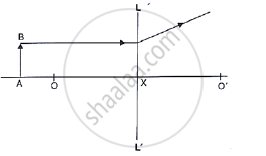
Study the diagram shown in Fig. 5.56
what are the two other characteristics of the image?
In the following diagram , the object and the image formed by the respective lenses are shown. Complete the ray diagram, and locate the focus. Find the focal length of the lens.

Make the rrect choices in the following items :
An object is placed 50 cm from a connverging lens of focal length 30 cm. The image produced would be
A lens forms the image of an object placed at a distance of 45 cm from it on a screen placed at a distance 90 cm on the other side of it. Name the kind of lens.
Name the subjective property of light related to its wavelength.
The diagram showed a lens as a combination of one glass block and two prisms. Complete the ray diagram and show the part of the incident ray AB after passing through the lens.
(i) Name of the lens formed by the combination.
(ii) What is the line XX’ called?
(iii) Mark the focus F.

In the following diagram, L1 and L2 are the two convex lense placed at separation equal to the sum of focal lengths of the two lenses. A and B are the two rays of light incident on the lens L1. Complete the path of rays till they emerge out of the lens L2.

What principles have you used in completing the diagram?
