Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The diagram given below shows the position of an object OA in relation to a converging lens L whose foci are at F1 and F2.
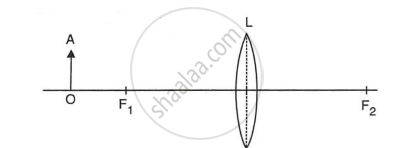
- Draw two rays to locate the position of the image.
- State the position of the image with reference to the lens.
- Describe three characteristics of the image.
- Describe how the distance of the image from the lens and its size change as the object is moved towards F1.
उत्तर
- The position of image A1B1 is located.
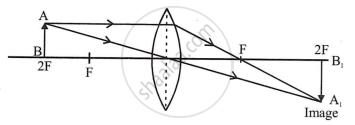
- The image is formed beyond 2F2 on the other side of the lens.
- Image is real inverted, beyond 2f and enlarged.
- Size of image increases and distance of image from the lens increases.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
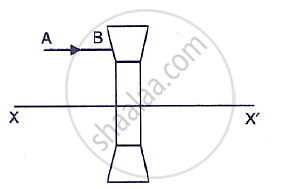
The diagram below shows a lens as a combination of a glass slab and two prisms.
- Name the lens formed by the combination.
- What is the line XX’ called?
- Complete the path of the incident ray AB after passing through the lens.
- The final emergent ray either meets XX’ at a point or appears to come from a point on XX’. Label it as F. What is this point called?
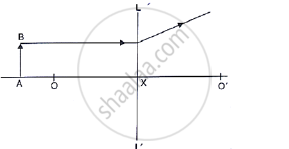
Study the diagram shown in Fig. 5.56
Complete the diagram to show the formation of image A’B’ of the object AB of same size.
A ray of light incident at the optical centre of lens, passes undeviated after refraction.
(a) Draw a sketch to show how a lens is able to produce an image of the sun on a paper screen.
(b)(i) Would you regard the rays from the sun as being divergent, parallel or convergent?
(ii) What is the name given to the point where such rays meet after they have passed through the lens?
(iii) How does the image of the sun sometimes burn a paper screen?
Make the rrect choices in the following items :
An object is placed 50 cm from a connverging lens of focal length 30 cm. The image produced would be
Make the correct choices in the following items :
The image formed by a diverging lens, shown in fig, , is
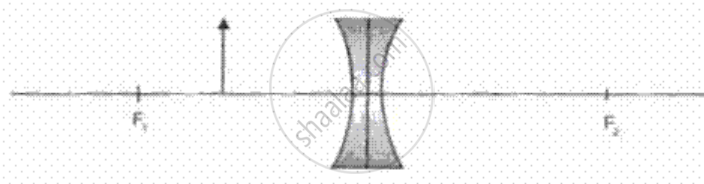
Fig. shows two rays of light Op and OQ coming from an object at the bottom of a pond, incident on the water surface.
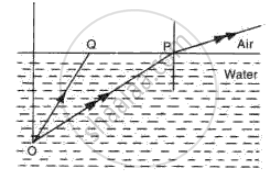
(a) Mark on the diagram
(i) The angle of incidence of ray OP,
(ii) The angle of refraction of ray Op,
(iii) The position of image of the object as seen from above.
(iv) An approximate path of the ray OQ.
(b) Explain, why do the rays of light change directions on passing from water to air.
(c) A fish in water sees everything outside the water by rays of light entering its eye in a small cone of light. Draw a diagram and explain how does this happen.
How will you differentiate between a convex and a concave lens by looking at a distant object.
When does a ray of light falling on a lens pass through it undeviated?
