Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
What are the three principal rays that are drawn to construct the ray diagram for the image formed by a lens? Draw diagrams to support your answer.
Solution
(i) A ray of light incident at the optical centre O of the lens passes undeviated through the lens.
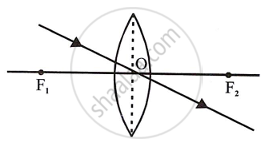
Convex lens
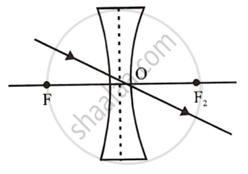
Concave lens
(ii) A ray of light incident parallel to the principal axis of the lens, after refraction passes through the second focus F2 (in a convex lens) or appears to come from the second focus F2 (in a concave lens).
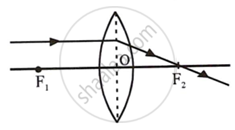
Convex lens
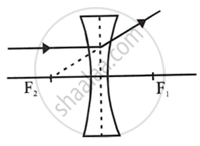
Concave lens
(iii) A ray of light passing through the first focus F1 (in a convex lens) or directed towards the first focus F1 (in a concave lens), emerges parallel to the principal axis after refraction.
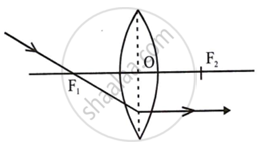
Convex lens
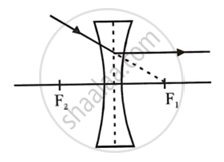
Concave lens
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
An image formed by a concave ______ cannot be obtained on a screen.
A real image cannot be obtained on a screen.
State two differences between a convex and a concave lens.
Which type of lens forms always a virtual image?
A diverging mirror of radius of curvature 40 cm forms an image which is half the height of the object. Find the object and image positions.
Explain why, a stick half immersed in water appears to be bent at the surface. Draw a labelled diagram to illustrate your answer.
If a spherical lens has a power of, −0.25 D, the focal length of this lens will be :
(a) −4 cm
(b) −400 mm
(c) −4 m
(d) −40 cm
A convex lens forms an image of an object equal to the size of the object. Where is the object placed in front of the lens?
Complete the ray diagram to show how the rays pass into and out of the lens?

Which diagram shows image formation of an object on a screen by a converging lens?
