Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What are the three principal rays that are drawn to construct the ray diagram for the image formed by a lens? Draw diagrams to support your answer.
उत्तर
(i) A ray of light incident at the optical centre O of the lens passes undeviated through the lens.
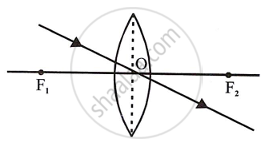
Convex lens
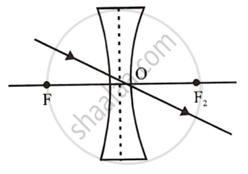
Concave lens
(ii) A ray of light incident parallel to the principal axis of the lens, after refraction passes through the second focus F2 (in a convex lens) or appears to come from the second focus F2 (in a concave lens).
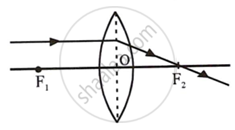
Convex lens
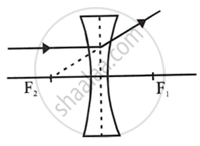
Concave lens
(iii) A ray of light passing through the first focus F1 (in a convex lens) or directed towards the first focus F1 (in a concave lens), emerges parallel to the principal axis after refraction.
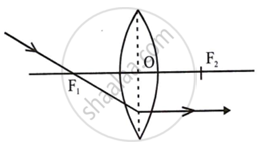
Convex lens
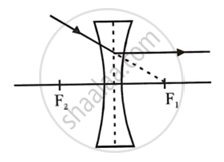
Concave lens
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The distance between principal focus and optical centre of the lens is _________.
- diameter
- focal length
- principal axis
- optical centre
A concave lens always forms a virtual image.
A real image cannot be obtained on a screen.
Which type of lens forms always a virtual image?
Explain why, a stick half immersed in water appears to be bent at the surface. Draw a labelled diagram to illustrate your answer.
Two lenses A and B have power of (i) +2D and (ii) −4D respectively. What is the nature and focal length of each lens?
If a spherical lens has a power of, −0.25 D, the focal length of this lens will be :
(a) −4 cm
(b) −400 mm
(c) −4 m
(d) −40 cm
A lens forms the image of an object placed at a distance 15 cm from it, at a distance 60 cm in front of it. Find the nature of image.
My grandfather uses a bifocal lens in his spectacle. Explain why.
Which diagram shows image formation of an object on a screen by a converging lens?
