Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Solution
The electromagnetic radiations of wavelength from 100 Å to 4000 Å are called the ultraviolet radiations.
Detection: If the different radiations from the red part of the spectrum to the violet end and beyond it are made incident on the silver-chloride solution, it is observed that from the red end to the violet, the solution remains almost unaffted. However just beyond the violet end, it first turns violet and finally it becomes dark brown (or black). thus, there exist certain radiations beyond the violet end of the spectrum, which are chemically more active than the visible light. Thses radiations are called the ultraviolet radiations.
Two properties of ultraviolet radiation:
1. Ultraviolet radiation can pass through quartz, but they are absorbed by glass.
2. They are usually scattered ny the dust particles present in the atmosphere.
one use of ultraviolet radiation:
in producing, Vitamin D, in food of plans and animals.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A wave has wavelength 50 Å.
- Name the wave.
- State its speed in vacuum.
- State its one use.
Name the electromagnetic radiations used for (a) water purification, and (b) eye surgery.
The wavelength of X-rays is 0.01 Å. Calculate its frequency. State the assumption made, if any.
How are X-rays produced?
To which regions of the electromagnetic spectrum do the following wavelengths belong:
(a) 250 nm
(b) 1500 nm
Name the radiations used for the detection of fracture in bones.
Answer briefly.
Why light waves travel in a vacuum whereas sound waves cannot?
Which of the following is a tool used for separating the different color wavelengths from each other?
Which one of the following electromagnetic radiation has the least wavelength?
In an atom X, electrons absorb the energy from an external source. This energy “excites” the electrons from a lower-energy level to a higher-energy level around the nucleus of the atom. When electrons return to the ground state, they emit photons.
The figure below is the energy level diagram of atom X with three energy levels, E1 = 0.00eV, E2 = 1.78eV and E3 = 2.95eV. The ground state is considered 0 eV for reference. The transition of electrons takes place between levels E1 and E2.
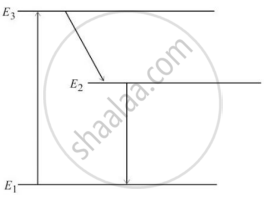
- What wavelength of radiation is needed to excite the atom to energy level E2 from E1?
- Suppose the external source has a power of 100 W. What would be the rate of photon emission?
