Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
In an atom X, electrons absorb the energy from an external source. This energy “excites” the electrons from a lower-energy level to a higher-energy level around the nucleus of the atom. When electrons return to the ground state, they emit photons.
The figure below is the energy level diagram of atom X with three energy levels, E1 = 0.00eV, E2 = 1.78eV and E3 = 2.95eV. The ground state is considered 0 eV for reference. The transition of electrons takes place between levels E1 and E2.
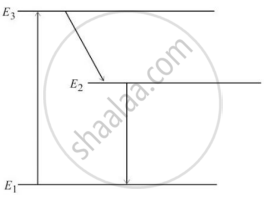
- What wavelength of radiation is needed to excite the atom to energy level E2 from E1?
- Suppose the external source has a power of 100 W. What would be the rate of photon emission?
Solution
(1) To start the laser, the molecule will have to be excited from E1 to E3. The wavelength required is
λ = `("hc")/(Delta"E")`
= `(1.24 xx 10^(-6))/2.95`
= 420.3 nm
Laser transition takes place between E1 and E2. So the wavelength of the beam of laser-produced will be
λ = `("hc")/(Delta"E")`
= `(1.24 xx 10^(-6))/1.78`
= 696.6 nm
(2) energy of photon = 1.78 eV
= 1.78 × 1.602 × 10-19 J
= 2.8516 × 10-19 J
photons emitted per second = `"power (energy emitted per second)"/"energy of each photon"`
= `(100 "W")/(2.8516 xx 10^(-19) "J")`
= 3.506 × 1020
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
X-ray from a Coolidge tube is incident on a thin aluminium foil. The intensity of the X-ray transmitted by the foil is found to be I0. The heating current is increased to increase the temperature of the filament. The intensity of the X-ray transmitted by the foil will be
(a) zero
(b) < I0
(c) I0
(d) > I0
The Kα and Kβ X-rays of molybdenum have wavelengths 0.71 A and 0.63 A respectively. Find the wavelength of Lα X-ray of molybdenum.
(Use Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js= 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
If the operating potential in an X-ray tube is increased by 1%, by what percentage does the cutoff wavelength decrease?
(Use Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js= 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
Name the scientist who discovered
X-rays
-
- Calculate the speed of the wave.
- Name the medium through which it is traveling.
Solve the numerical problem.
Calculate the frequency in MHz of a radio wave of wavelength 250 m. Remember that the speed of all EM waves in a vacuum is 3.0 × 108 m/s.
Which of the following is a tool used for separating the different color wavelengths from each other?
What is time period of the light for which the eye is most sensitive?
Electromagnetic waves with wavelength
- λ1 is used in satellite communication.
- λ2 is used to kill germs in water purifies.
- λ3 is used to detect leakage of oil in underground pipelines.
- λ4 is used to improve visibility in runways during fog and mist conditions.
- Identify and name the part of electromagnetic spectrum to which these radiations belong.
- Arrange these wavelengths in ascending order of their magnitude.
- Write one more application of each.
