Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
X-ray from a Coolidge tube is incident on a thin aluminium foil. The intensity of the X-ray transmitted by the foil is found to be I0. The heating current is increased to increase the temperature of the filament. The intensity of the X-ray transmitted by the foil will be
(a) zero
(b) < I0
(c) I0
(d) > I0
Options
zero
< I0
I0
> I0
Solution
> I0.
We know that the intensity of an X-ray is directly proportional to the current through the X-ray tube. If the filament current is increased to increase the temperature of the filament, more electrons will be emitted from the filament per unit time. As a result, current in the X-ray tube will increase and consequently, the intensity of the X-ray will also increase.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Why are microwaves considered suitable for radar systems used in aircraft navigation?
What role dose infra-red radiation play in maintain the Earth’s warmth
Name the phenomenon which shows the quantum nature of electromagnetic radiation.
Name the region beyond the red end of the spectrum.
Name of physical quantity which remains same for microwaves of wavelength 1 mm and UV radiations of 1600 Å in vacuum.
How are X-rays produced?
Which part of electromagnetic spectrum is used in radar systems?
When a Coolidge tube is operated for some time it becomes hot. Where does the heat come from?
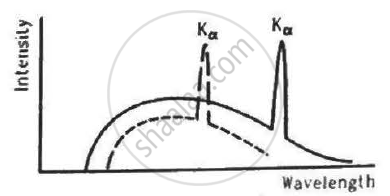
The figure shows the intensity-wavelength relations of X-rays coming from two different Coolidge tubes. The solid curve represents the relation for the tube A in which the potential difference between the target and the filament is VA and the atomic number of the target material is ZA. These quantities are VB and ZB for the other tube. Then,
50% of the X-ray coming from a Coolidge tube is able to pass through a 0.1 mm thick aluminium foil. The potential difference between the target and the filament is increased. The thickness of the aluminium foil that will allow 50% of the X-ray to pass through will be
The potential difference applied to an X-ray tube is increased. As a result, in the emitted radiation,
(a) the intensity increases
(b) the minimum wavelength increases
(c) the intensity remains unchanged
(d) the minimum wavelength decreases.
The electric current in an X-ray tube (from the target to the filament) operating at 40 kV is 10 mA. Assume that on an average, 1% of the total kinetic energy of the electron hitting hte target are converted into X-rays.
(a) What is the total power emitted as X-rays and (b) how much heat is produced in the target every second?
The electron beam in a colour TV is accelerated through 32 kV and then strikes the screen. What is the wavelength of the most energetic X-ray photon?
(Use Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js= 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
Name the scientist who discovered Microwaves
Name the scientist who discovered Infra-red waves
What are the ultraviolet rays?
Calculate the wavelength of a microwave of a frequency of 8.0 GHz.
The electric field intensity produced by the radiations coming from 100 W bulb at a 3 m distance is E. The electric field intensity produced by the radiations coming from 50 W bulb at the same distance is ______.
Electromagnetic waves with wavelength
- λ1 is used in satellite communication.
- λ2 is used to kill germs in water purifies.
- λ3 is used to detect leakage of oil in underground pipelines.
- λ4 is used to improve visibility in runways during fog and mist conditions.
- Identify and name the part of electromagnetic spectrum to which these radiations belong.
- Arrange these wavelengths in ascending order of their magnitude.
- Write one more application of each.
What is the wavelength range of electromagnetic radiation used in radio broadcast?
