Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
X-ray from a Coolidge tube is incident on a thin aluminium foil. The intensity of the X-ray transmitted by the foil is found to be I0. The heating current is increased to increase the temperature of the filament. The intensity of the X-ray transmitted by the foil will be
(a) zero
(b) < I0
(c) I0
(d) > I0
पर्याय
zero
< I0
I0
> I0
उत्तर
> I0.
We know that the intensity of an X-ray is directly proportional to the current through the X-ray tube. If the filament current is increased to increase the temperature of the filament, more electrons will be emitted from the filament per unit time. As a result, current in the X-ray tube will increase and consequently, the intensity of the X-ray will also increase.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Name the parts of the electromagnetic spectrum which is
used as a diagnostic tool in medicine.
Write in brief, how these waves can be produced.
A plane electromagnetic wave travels in vacuum along z-direction. What can you say about the directions of its electric and magnetic field vectors? If the frequency of the wave is 30 MHz, what is its wavelength?
The terminology of different parts of the electromagnetic spectrum is given in the text. Use the formula E = hv (for energy of a quantum of radiation: photon) and obtain the photon energy in units of eV for different parts of the electromagnetic spectrum. In what way are the different scales of photon energies that you obtain related to the sources of electromagnetic radiation?
What is the range of the wavelength of the following electromagnetic waves?
(a) Visible.
Name two electromagnetic waves of frequency smaller than that of violet light. State one use of each.
If the potential difference applied to the tube is doubled and the separation between the filament and the target is also doubled, the cutoff wavelength
Moseley's Law for characteristic X-ray is √v = a(Z − b). Here,
Cutoff wavelength of X-rays coming from a Coolidge tube depends on the
(a) target material
(b) accelerating voltage
(c) separation between the target and the filament
(d) temperature of the filament.
An X-ray tube operates at 40 kV. Suppose the electron converts 70% of its energy into a photon at each collision. Find the lowest there wavelengths emitted from the tube. Neglect the energy imparted to the atom with which the electron collides.
(Use Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js= 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
State the name and the range of wavelength of the invisible electromagnetic waves beyond the red end of the visible spectrum.
Name two sources of infrared radiation.
An electron beam is accelerated by a potential difference V to hit a metallic target to produce X-rays. It produces continuous as well as characteristic X-rays. If λmin is the smallest possible wavelength of X-ray in the spectrum, the variation of log λmin with log V is correctly represented in:
The ozone layer absorbs
If λv, λx and λm Am represents the wavelength of visible light, x-ray and microwaves respectively, then ______.
Given below in the left column are different modes of communication using the kinds of waves given in the right column.
| A. | Optical Fibre Communication |
P. | Ultrasound |
| B. | Radar | Q. | Infrared Light |
| C. | Sonar | R. | Microwaves |
| D. | Mobile Phones | S. | Radio Waves |
From the options given below, find the most appropriate match between entries in the left and the right column.
Identify the electromagnetic wave whose wavelength range is from about 10-12 m to about 10-8 m. Write one use of this.
Name one radiation having the wavelength longer than the wavelength of these radiations.
What happens when an electron collides with a positron?
Name the electromagnetic radiation that has been used in obtaining the image below.
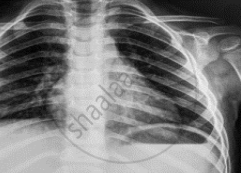
In an atom X, electrons absorb the energy from an external source. This energy “excites” the electrons from a lower-energy level to a higher-energy level around the nucleus of the atom. When electrons return to the ground state, they emit photons.
The figure below is the energy level diagram of atom X with three energy levels, E1 = 0.00eV, E2 = 1.78eV and E3 = 2.95eV. The ground state is considered 0 eV for reference. The transition of electrons takes place between levels E1 and E2.
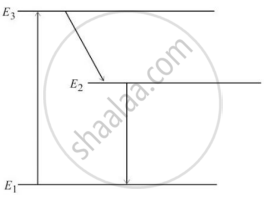
- What wavelength of radiation is needed to excite the atom to energy level E2 from E1?
- Suppose the external source has a power of 100 W. What would be the rate of photon emission?
