Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
50% of the X-ray coming from a Coolidge tube is able to pass through a 0.1 mm thick aluminium foil. The potential difference between the target and the filament is increased. The thickness of the aluminium foil that will allow 50% of the X-ray to pass through will be
पर्याय
zero
< 0.1 mm
0.1 mm
> 0.1 mm
उत्तर
> 0.1 mm
As we increase the accelerating potential between the filament and the target, the penetrating power of the X-ray will increase. As a result, the fraction of the X-ray passing through the foil will increase. But it is given that the same fraction of the X-ray is passing. Therefore, the thickness of the aluminium foil should be increased to maintain the same fraction of the X-ray that will pass through the foil.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Optical and radio telescopes are built on the ground but X-ray astronomy is possible only from satellites orbiting the earth. Why?
What is the range of the wavelength of the following electromagnetic waves?
(a) Visible.
Give one use of gamma rays.
The wavelength of X-rays is 0.01 Å. Calculate its frequency. State the assumption made, if any.
Name of physical quantity which remains same for microwaves of wavelength 1 mm and UV radiations of 1600 Å in vacuum.
Can X-rays be used for photoelectric effect?
The Kα and Kβ X-rays of molybdenum have wavelengths 0.71 A and 0.63 A respectively. Find the wavelength of Lα X-ray of molybdenum.
When 40 kV is applied across an X-ray tube, X-ray is obtained with a maximum frequency of 9.7 × 1018 Hz. Calculate the value of Planck constant from these data.
(Use Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js= 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
A free atom of iron emits Kα X-rays of energy 6.4 keV. Calculate the recoil kinetic energy of the atom. Mass of an iron atom = 9.3 × 10−26 kg.
(Use Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js= 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
Calculate the shortest wavelength of electromagnetic radiation present in Balmer series of hydrogen spectrum.
Identify the part of the electromagnetic spectrum used in
(i) radar and
(ii) eye surgery. Write their frequency range.
Solve the numerical problem.
The speed of light is 3 × 108 m/s. Calculate the frequency of red light of a wavelength of 6.5 × 10−7 m.
Light of wavelength `3500A` is incident on two metals A and B whose work functions are 3.2 eV and 1.9 eV respectively. Which metal will emit photoelectrons?
Microwaves are electromagnetic waves with frequency in the range of.
Which is the correct ascending order of wavelengths?
What is the speed of radio waves in vacuum?
Name the electromagnetic radiation that has been used in obtaining the image below.
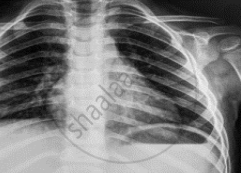
In an atom X, electrons absorb the energy from an external source. This energy “excites” the electrons from a lower-energy level to a higher-energy level around the nucleus of the atom. When electrons return to the ground state, they emit photons.
The figure below is the energy level diagram of atom X with three energy levels, E1 = 0.00eV, E2 = 1.78eV and E3 = 2.95eV. The ground state is considered 0 eV for reference. The transition of electrons takes place between levels E1 and E2.
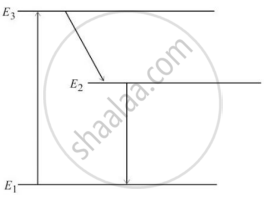
- What wavelength of radiation is needed to excite the atom to energy level E2 from E1?
- Suppose the external source has a power of 100 W. What would be the rate of photon emission?
