Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
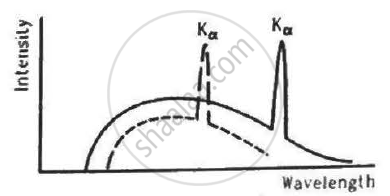
The figure shows the intensity-wavelength relations of X-rays coming from two different Coolidge tubes. The solid curve represents the relation for the tube A in which the potential difference between the target and the filament is VA and the atomic number of the target material is ZA. These quantities are VB and ZB for the other tube. Then,
Options
VA > VB, ZA > ZB
VA > VB, ZA < ZB
VA < VB, ZA > ZB
VA > VB, ZA < ZB
Solution
VA > VB, ZA < ZB
It is clear from the figure that the X-ray of tube A has less cutoff wavelength than the X-ray of tube B.
`therefore lambda_A < lambda_B`
Using Moseley's Law,
`Z_A < Z_B`
`lambda ∝ 1/V` , where V is the voltage applied in the X-ray tube.
`therefore V_A > V_B`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Why are microwaves considered suitable for radar systems used in aircraft navigation?
State Moseley's law
What is the range of the wavelength of the following electromagnetic waves?
(a) Visible.
What is the range of the wavelength of the following electromagnetic waves?
(A) Radio waves.
The energy of a photon of a characteristic X-ray from a Coolidge tube comes from
Moseley's Law for characteristic X-ray is √v = a(Z − b). Here,
What potential difference should be applied across an X-ray tube to get X-ray of wavelength not less than 0.10 nm? What is the maximum energy of a photon of this X-ray in joule?
(Use Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js= 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
Find the maximum potential difference which may be applied across an X-ray tube with tungsten target without emitting any characteristic K or L X-ray. The energy levels of the tungsten atom with an electron knocked out are as follows.
| Cell containing vacancy | K | L | M |
| Energy in keV | 69.5 | 11.3 | 2.3 |
Heat at the rate of 200 W is produced in an X-ray tube operating at 20 kV. Find the current in the circuit. Assume that only a small fraction of the kinetic energy of electrons is converted into X-rays.
The electron beam in a colour TV is accelerated through 32 kV and then strikes the screen. What is the wavelength of the most energetic X-ray photon?
(Use Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js= 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
Write the range of the wavelength of the following electromagnetic radiations:
(a) Infrared rays
(b) Ultraviolet rays
(c) γ -rays
Write one use of each of the above.
-
- Calculate the speed of the wave.
- Name the medium through which it is traveling.
Name any two electromagnetic waves which have a frequency higher than that of violet light. State one use of each.
Answer briefly.
Can we produce a pure electric or magnetic wave in space? Why?
Light of wavelength `3500A` is incident on two metals A and B whose work functions are 3.2 eV and 1.9 eV respectively. Which metal will emit photoelectrons?
A car is moving towards a high cliff. The car driver sounds a horn of frequency f. The reflected sound heard by the driver has a frequency 2f. If v be the velocity of sound, then the velocity of the car, in the same velocity units, will be:
The frequency of x-rays, y-rays and ultraviolet rays are respectively a, b and c. Then:-
The area to be covered for T.V telecast is doubled then the height of transmitting antenna (T.V tower) will have to be:-
The frequency of e. m waves which is best suited .to observed of radius 3 × 10–4 his of the order of
What is the speed of radio waves in vacuum?
