ISC (Science)
Academic Year: 2024-2025
Date: April 2025
Advertisements
- You are allowed an additional 15 minutes to read the question paper.
- You must NOT start writing during reading time.
- This question paper has 12 printed pages and 20 questions.
- There are four sections in the paper: A, B, C and D. Internal choices have been provided in two questions each in Sections B, C and D.
- Section A consists of one question having fourteen sub-parts of one mark each.
- Section B consists of seven questions of two marks each.
- Section C consists of nine questions of three marks each.
- Section D consists of three questions of five marks each.
- Answer all questions.
- The intended marks for questions are given in brackets [ ].
- A list of useful constants and relations is given at the end of this paper.
- A simple scientific calculator without a programmable memory may be used for calculations.
The figure below shows a circuit containing an ammeter A, a galvanometer G and a plug key K. When the key is closed:
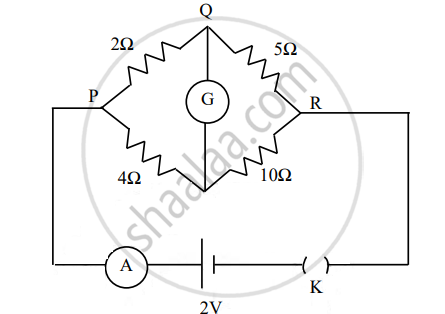
both G and A show deflections.
neither G nor A shows deflection.
G shows deflection but A does not.
A shows deflection but G does not.
Chapter: [0.031] Moving Charges and Magnetism
A circular coil having N turns of radius R carrying a current I is used to produce a magnetic field B at its centre O.
If this coil is opened and rewound such that the radius of the newly formed coil is 2R, carrying the same current I, what will be the magnetic field at the centre O?
2B
B
`"B"/2`
`"B"/4`
Chapter: [0.031] Moving Charges and Magnetism
Magnetic susceptibility of a diamagnetic substance ______.
decreases with the increase in its temperature.
is not affected by the change in its temperature.
increases with increase in its temperature.
first increases then decreases with increase in its with temperature.
Chapter: [0.032] Magnetism and Matter
The de Broglie wavelength of an electron in the first Bohr’s orbit of hydrogen atom is equal to ______.
diameter of the first orbit.
circumference of the first orbit.
radius of the second orbit.
`"h"/(2\pi)`
Chapter: [0.081] Atoms
An ideal PN junction diode offers ______.
zero resistance in forward as well as reverse bias.
infinite resistance in forward as well as reverse bias.
zero resistance in forward, but infinite resistance in reverse bias.
infinite resistance in forward, but zero resistance in reverse bias.
Chapter: [0.09] Electronic Devices
Assertion: An astronomical telescope has an objective lens having large focal length.
Reason: Magnifying power of an astronomical telescope varies directly with focal length of the objective lens.
Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation for Assertion.
Both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation for Assertion.
Assertion is false and Reason is true.
Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Chapter: [0.061] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Assertion: If critical angle of glass-air pair `("μg" = 3/2)` is θ1 and that of water-air pair `("μw" = 4/3)` is θ2, then the critical angle for the water-glass pair will lie between θ1 and θ2.
Reason: A medium is optically denser if its refractive index is greater.
Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation for Assertion.
Both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation for Assertion.
Assertion is false and Reason is true.
Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Chapter: [0.061] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Current I flowing through a metallic wire is gradually increased. Show graphically how heating power (P) developed in it varies with the current (I).
Chapter: [0.02] Current Electricity
Explain why core of a transformer is always laminated.
Chapter: [0.042] Alternating Current
Why does a car driver use a convex mirror as a rear-view mirror?
Chapter: [0.061] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Represent diagrammatically how the incident planar wavefronts of wavelength λ pass through an aperture of size d, when d is approximately equal to λ.
Chapter: [0.062] Wave Optics
What is meant by “Dual nature of matter”?
Chapter: [0.07] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
What happens when an electron collides with a positron?
Chapter: [0.05] Electromagnetic Waves
What energy conversion takes place in a solar cell?
Chapter: [0.09] Electronic Devices
A dielectric slab of dielectric constant K and thickness t is introduced between the two plates of a capacitor of plate-separation d (>t) and common area A. The capacitance of this system is given as:
`C = (∈_o"A")/((d-t)+(t/k))`
How does the capacitance C modify in each of the following cases?
- The dielectric slab covers half the distance of separation between the two plates.
- The whole space between the plates is filled with the dielectric.
Chapter: [0.012] Electrostatic Potential, Potential Energy and Capacitance
In the Figure below, the current-voltage graphs for a conductor are given at two different temperatures, T1 and T2.
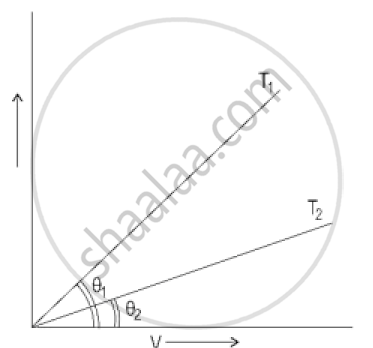
- At which temperature T1 or T2 is the resistance higher?
- Which temperature (T1 or T2) is higher?
Chapter: [0.042] Alternating Current
Advertisements
Arrangement of an oxygen ion and two hydrogen ions in a water molecule is shown in figure below.
Calculate electric dipole moment of water molecule. Express your answer in terms of e (charge on hydrogen ion), l and θ.
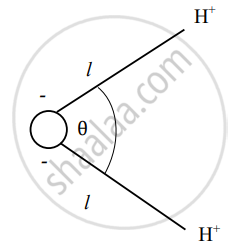
Chapter: [0.011000000000000001] Electric Charges and Fields
The figure below shows a part of an electric circuit.

- Apply Kirchhoff’s junction rule to the junction A to find current flowing through the 5Ω resistor.
- Apply Kirchhoff’s loop rule to the loop ABDA to find current flowing through the 7Ω resistor.
Chapter:
In a potentiometer, a cell is balanced against 110 cm when the circuit is open. A cell is balanced at 100 cm when short-circuited through a resistance of 10 Ω. Find the internal resistance of the cell.
Chapter: [0.02] Current Electricity
The figure below are two long, parallel wires carrying current in the same direction such that I1 < I2.
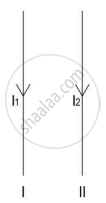
- In which direction will wire I1 move?
- If the direction of the current I2 is reversed, in which direction will the wire I1 move now?
Chapter: [0.031] Moving Charges and Magnetism
The focal length of a double convex lens is equal to the radius of curvature of either surface. What is the refractive index of its material?
Chapter: [0.061] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
What is meant by a thin prism?
Chapter: [0.061] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Name the electromagnetic radiation that has been used in obtaining the image below.
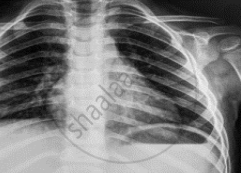
Chapter: [0.05] Electromagnetic Waves
What is the wavelength range of electromagnetic radiation used in radio broadcast?
Chapter: [0.05] Electromagnetic Waves
How does stopping potential in photoelectric emission vary if the intensity of the incident radiation increases?
Chapter: [0.07] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
How does stopping potential in photoelectric emission vary if the frequency of incident radiation decreases?
Chapter: [0.07] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
“A uniformly charged conducting spherical shell for the points outside the shell behaves as if the entire charge of the shell is concentrated at its centre”. Show this with the help of a proper diagram and verify this statement.
Chapter: [0.011000000000000001] Electric Charges and Fields
Study the two circuits shown in the figure below. The cells in the two circuits are identical to each other. The resistance of the load resistor R is the same in both circuits.
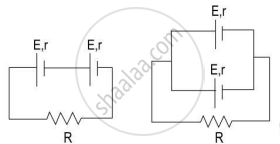
If the same current flows through the resistor R in both circuits, calculate the internal resistance of each cell in terms of the resistance of resistor R. Show your calculations.
Chapter: [0.02] Current Electricity
The drift velocity of electrons in a conductor connected to a battery is given by vd = `(−"eE" τ)/"m"`. Here, e is the charge of the electron, E is the electric field, τ is the average time between collisions and m is the mass of the electron.
Based on this, answer the following:
- How does the drift velocity change with a change in the potential difference across the conductor?
- A copper wire of length 'l' is connected to a source. If the copper wire is replaced by another copper wire of the same area of cross-section but of length '4l', how will the drift velocity change? Explain your answer.
Chapter: [0.02] Current Electricity
A galvanometer of resistance 100 Ω gives a full-scale deflection for a potential difference of 200 mV.
- What must be the resistance connected to convert the galvanometer into an ammeter of the range 0-200 mA?
- Determine resistance of the ammeter.
Chapter: [0.031] Moving Charges and Magnetism
Advertisements
A student records the following data for the magnitudes (B) of the magnetic field at axial points at different distances x (See figure given below) from the centre O of a circular coil of radius a carrying a current I. Verify (for any two) that these observations are in good agreement with the expected theoretical values of B.
| x | x = 0 | x = a | x = 2a | x = 3a |
| B | B0 | `("B"_0)/(2√2)` | `("B"_0)/(5√5)` | `("B"_0)/(10√10)` |
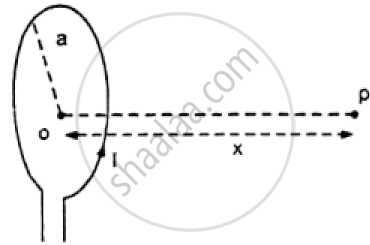
Chapter: [0.032] Magnetism and Matter
An electron moving along positive X axis with a velocity of 8 ×107ms-1 enters a region having uniform magnetic field B = 1.3 × 10-3 T along positive Y axis.
- Explain why the electron describes a circular path.
- Calculate the radius of the circular path described by the electron.
Chapter: [0.031] Moving Charges and Magnetism
With the help of a neatly drawn labelled diagram, prove the law of reflection on the basis of Huygen’s wave theory.
Chapter: [0.062] Wave Optics
A lens of focal length f is divided into two equal parts and then these parts are put in a combination as shown in the figure below.
- What is the focal length of L1?
- What is the focal length of the final combination?
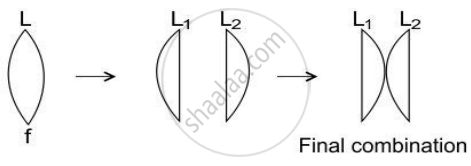
Chapter: [0.061] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
In Young’s double slit experiment, how is interference pattern affected when the following changes are made:
- Slits are brought closer to each other.
- Screen is moved away from the slits.
- Red coloured light is replaced with blue coloured light.
Chapter: [0.062] Wave Optics
- A virologist studies details of a virus with the help of an instrument. Name the instrument used by him.
- Draw a labelled ray diagram of an image formed by this instrument, assuming
- a small upright object.
- image lies at least distance of distinct vision.
Chapter: [0.061] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
The graphs below show the variation of the stopping potential VS with the frequency (ν) of the incident radiations for two different photosensitive materials M1 and M2.
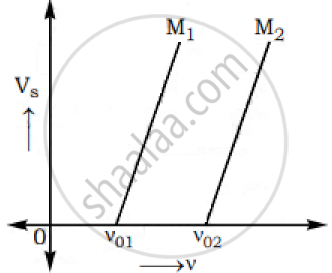
Express work function for M1 and M2 in terms of Planck’s constant(h) and Threshold frequency and charge of the electron (e).
If the values of stopping potential for M1 and M2 are V1 and V2 respectively then show that the slope of the lines equals to `(V_1-V_2)/(V_(01)-V_(02))` for a frequency,
ν > ν02 and also ν > ν01
Chapter: [0.07] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
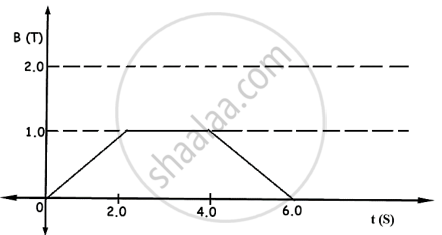
The magnetic field through a single loop of wire, 12 cm in radius and 8·5 Ω resistance, changes with time as shown in graph below. The magnetic field is perpendicular to the plane of the loop.
- Find the induced emf for the time intervals 0 to 2.0 s, 2.0 to 4.0 s, and 4.0 to 6.0 s.
- Hence, plot induced current as a function of time.
Chapter: [0.032] Magnetism and Matter
Three students, X, Y and Z performed an experiment for studying the variation of a.c. with frequency in a series LCR circuit and obtained the graphs as shown below. They all used
- an AC source of the same emf and
- inductance of the same value.
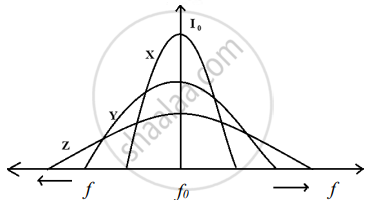
- Who used minimum resistance?
- In which case will the quality Q factor be maximum?
- What did the students conclude about the nature of impedance at resonant frequency (f0)?
- An ideal capacitor is connected across 220V, 50Hz, and 220V, 100Hz supplies. Find the ratio of current flowing through it in the two cases.
Chapter: [0.042] Alternating Current
Find the binding energy per nucleon of 235U based on the information given below.
| Mass(u) | |
| mass of neutral `""_92^235"U"` | 235.0439 |
| mass of a proton | 1.0073 |
| mass of a neutron | 1.0087 |
Chapter: [0.08199999999999999] Nuclei
Find the energy released during the following fission reaction.
\[\ce{_92^235U + _0^1n-> _92^236U->_36^90Kr + _56^143Ba + 3 _0^1n}\]
| Mass(u) | |
| 235U | 235.0439 |
| 90Kr | 89.9195 |
| 143Ba | 142.9206 |
| 1n | 1.0087 |
Chapter: [0.08199999999999999] Nuclei
During Rutherford’s gold foil experiment, it was observed that most of the α-particles did not deflect. However, some showed a deflection of 180°.
What hypothesis was made to justify the deflection of α-particle by 180°?
Chapter: [0.081] Atoms
Define unified atomic mass unit.
Chapter: [0.08199999999999999] Nuclei
Calculate the energy equivalent of unified atomic mass unit.
Chapter: [0.08199999999999999] Nuclei
In an atom X, electrons absorb the energy from an external source. This energy “excites” the electrons from a lower-energy level to a higher-energy level around the nucleus of the atom. When electrons return to the ground state, they emit photons.
The figure below is the energy level diagram of atom X with three energy levels, E1 = 0.00eV, E2 = 1.78eV and E3 = 2.95eV. The ground state is considered 0 eV for reference. The transition of electrons takes place between levels E1 and E2.
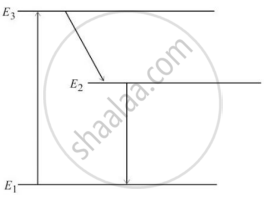
- What wavelength of radiation is needed to excite the atom to energy level E2 from E1?
- Suppose the external source has a power of 100 W. What would be the rate of photon emission?
Chapter: [0.05] Electromagnetic Waves
Sanya performed an experiment of obtaining characteristic curves of a junction diode. When she forward biased it, she found that beyond forward voltage V = Vk, the conductivity is very high. When she reverse biased the diode she found that a very small current (of about a few microamperes) flows in the diode. It remained constant even though she varied the voltage.
(i) In Figure 1 below, which one of the diodes is forward biased?
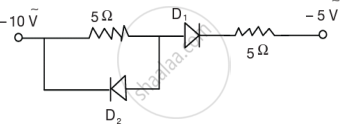
Figure 1
(ii) What is meant by a saturation current?
(iii) When applied voltage during forward bias is small, why does no current flow in the diode?
(iv) The circuit shown in Figure 2 below contains two diodes, each with a forward resistance of 50 Ω and with infinite resistance during reverse bias. If the battery voltage is 6V, then calculate the current through the 100 Ω resistance.
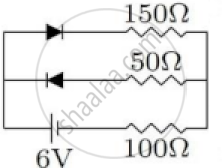
Figure 2
Chapter: [0.09] Electronic Devices
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
CISCE previous year question papers ISC Class 12 Physics (Theory) with solutions 2024 - 2025
Previous year Question paper for CISCE ISC Class 12 -2025 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Physics (Theory), you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of CISCE ISC Class 12.
How CISCE ISC Class 12 Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Physics (Theory) will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.
