Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A galvanometer of resistance 100 Ω gives a full-scale deflection for a potential difference of 200 mV.
- What must be the resistance connected to convert the galvanometer into an ammeter of the range 0-200 mA?
- Determine resistance of the ammeter.
Solution
(i) Given: G = 100 Ω; I = 200 mA;
Vg = 200 mV;
Resistance to be connected to the galvanometer to convert to an ammeter:
S = `("I"_"g""G")/(("I"-"I"_"g"))`
Here Ig= `("V"_"g")/"G"`
= `(200 " mV")/(100 " Ω")`
= 2 mA
S = `(2 × 10^(-3) × 100)/((0.2-0.002))`
S = 1.01 Ω
(ii) `1/"R" = 1/100 + 1/1.01`
R = 0.999 Ω
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Increasing the current sensitivity of a galvanometer may not necessarily increase its voltage sensitivity. Explain, giving reason.
Two moving coil meters, M1 and M2 have the following particulars:
R1 = 10 Ω, N1 = 30,
A1 = 3.6 × 10–3 m2, B1 = 0.25 T
R2 = 14 Ω, N2 = 42,
A2 = 1.8 × 10–3 m2, B2 = 0.50 T
(The spring constants are identical for the two meters).
Determine the ratio of
- current sensitivity and
- voltage sensitivity of M2 and M1.
A moving coil galvanometer has a coil of resistance 59 Ω. It shows a full-scale deflection for a current of 50 mA. How will you convert it to an ammeter having a range of 0 to 3A?
State how a moving coil galvanometer can be converted into an ammeter.
Explain the significance of a radial magnetic field when a current-carrying coil is kept in it.
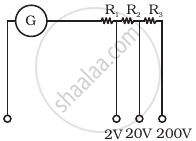
A multirange voltmeter can be constructed by using a galvanometer circuit as shown in figure. We want to construct a voltmeter that can measure 2V, 20V and 200V using a galvanometer of resistance 10Ω and that produces maximum deflection for current of 1 mA. Find R1, R2 and R3 that have to be used.
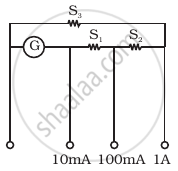
A multirange current meter can be constructed by using a galvanometer circuit as shown in figure. We want a current meter that can measure 10 mA, 100 mA and 1A using a galvanometer of resistance 10 Ω and that prduces maximum deflection for current of 1mA. Find S1, S2 and S3 that have to be used
A galvanometer shows full-scale deflection for current Ig. A resistance R1 is required to convert it into a voltmeter of range (0 - V) and a resistance R2 to convert it into a voltmeter of range (0 - 2V). Find the resistance of the galvanometer.
A moving coil galvanometer of resistance 55 Ω produces a full scale deflection for a current of 250 mA. How will you convert it into an ammeter with a range of 0 - 3A?
