Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A galvanometer of resistance 100 Ω gives a full-scale deflection for a potential difference of 200 mV.
- What must be the resistance connected to convert the galvanometer into an ammeter of the range 0-200 mA?
- Determine resistance of the ammeter.
उत्तर
(i) Given: G = 100 Ω; I = 200 mA;
Vg = 200 mV;
Resistance to be connected to the galvanometer to convert to an ammeter:
S = `("I"_"g""G")/(("I"-"I"_"g"))`
Here Ig= `("V"_"g")/"G"`
= `(200 " mV")/(100 " Ω")`
= 2 mA
S = `(2 × 10^(-3) × 100)/((0.2-0.002))`
S = 1.01 Ω
(ii) `1/"R" = 1/100 + 1/1.01`
R = 0.999 Ω
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Obtain the expression for current sensitivity of moving coil galvanometer.
A galvanometer of resistance G is converted into a voltmeter to measure upto V volts by connecting a resistance R1 in series with the coil. If a resistance R2 is connected in series with it, then it can measures upto V/2 volts. Find the resistance, in terms of R1 and R2, required to be connected to convert it into a voltmeter that can read upto 2 V. Also find the resistance G of the galvanometer in terms of R1 and R2
Draw a labelled diagram of a moving coil galvanometer. Describe briefly its principle and working.
A galvanometer has a resistance of 16Ω. It shows full scale deflection, when a current of 20 mA is passed through it. The only shunt resistance available is 0.06 which is not appropriate to convert a galvanometer into an ammeter. How much resistance should be connected in series with the coil of galvanometer, so that the range of ammeter is 8 A?
With the help of a neat and labelled diagram, explain the principle and working of a moving coil galvanometer ?
Outline the necessary steps to convert a galvanometer of resistance RG into an ammeter of a given range ?
The current sensitivity of a galvanometer increase by 20%. If its resistance also increases by 25%, the voltage sensitivity will ______.
A galvanometer having a coil resistance of 60 Ω shows full-scale deflection when a current of 1.0 amp passes through it. It can be converted into an ammeter to read currents up to 5.0 amp by:
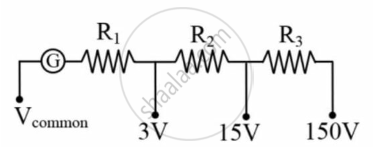
A voltmeter of variable ranges 3 V, 15 V, 150 V is to be designed by connecting resistances R1, R2, R3 in series with a galvanometer of resistance G = 20 Ω, as shown in Fig. The galvanometer gives full pass through its coil for 1 mA current i.e. "gives full pass through it's coil for 1 mA current". Then, the resistances R1, R2 and R3 (in kilo ohms) should be, respectively:
Assertion: When an electric current is passed through a moving coil galvanometer, its coil gets deflected.
Reason: A circular coil produces a uniform magnetic field around itself when an electric current is passed through it.
