Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A galvanometer of resistance G is converted into a voltmeter to measure upto V volts by connecting a resistance R1 in series with the coil. If a resistance R2 is connected in series with it, then it can measures upto V/2 volts. Find the resistance, in terms of R1 and R2, required to be connected to convert it into a voltmeter that can read upto 2 V. Also find the resistance G of the galvanometer in terms of R1 and R2
उत्तर
A high resistance that is connected in series with the galvanometer to convert it into voltmeter. The value of the resistance is given by
Here,
V = Potential difference across the terminals of the voltmeter
Ig = Current through the galvanometer
G = Resistance of the galvanometer
When resistance R1 is connected in series with the galvanometer,
When resistance R2 is connected in series with the galvanometer,
From (i) and (i), we get
The resistance R3 required to convert the given galvanometer into voltmeter of range 0 to 2V is given by
⇒R3=4(R1−R2)−(2R1−R2)=3R1−2R2
G in terms of R1 and R2 is given by
G=R1−2R2
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A rectangular coil of a moving coil galvanometer contains 50 turns each having area 12 cm2 . It is suspended in radial magnetic field 0.025 Wb/m2 by a fibre of twist constant 15 x10-10 Nm/degree. Calculate the sensitivity of the moving coil galvanometer.
An ideal voltmeter has _______.
(A) low resistance
(b) high resistance
(C) infinite resistance
(D) zero resistance
Why is it necessary to introduce a cylindrical soft iron core inside the coil of a galvanometer?
The AC voltage across a resistance can be measured using a ______.
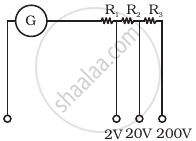
A multirange voltmeter can be constructed by using a galvanometer circuit as shown in figure. We want to construct a voltmeter that can measure 2V, 20V and 200V using a galvanometer of resistance 10Ω and that produces maximum deflection for current of 1 mA. Find R1, R2 and R3 that have to be used.
A moving coil galvanometer has 150 equal divisions. Its current sensitivity is 10-divisions per milliampere and voltage sensitivity is 2 divisions per millivolt. In order that each division reads 1 volt, the resistance in ohms needed to be connected in series with the coil will be ______.
A voltmeter has a range of 0 - 20 V and a resistance of 500 Q. Explain how can be used to measure voltages from 0 - 200 volt?
A moving coil galvanometer of resistance 55 Ω produces a full scale deflection for a current of 250 mA. How will you convert it into an ammeter with a range of 0 - 3A?
A galvanometer of resistance 100 Ω gives a full-scale deflection for a potential difference of 200 mV.
- What must be the resistance connected to convert the galvanometer into an ammeter of the range 0-200 mA?
- Determine resistance of the ammeter.
