Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A moving coil galvanometer of resistance 55 Ω produces a full scale deflection for a current of 250 mA. How will you convert it into an ammeter with a range of 0 - 3A?
उत्तर
Galvanometer - Ammeter
and shunt is parallel to galvanometer
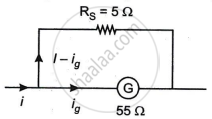
Rs(I - ig) = igG
`"R"_"s" = (250 xx 10^-3 xx 55)/(3 - 250 xx 10^-3)`
`"R"_"s" = 13.75/2.75`
Rs = 5 Ω
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The combined resistance of a galvanometer of resistance 500Ω and its shunt is 21Ω. Calculate the value of shunt.
Why does a galvanometer show a momentary deflection at the time of charging or discharging a capacitor? Write the necessary expression to explain this observation.
A galvanometer has a resistance of 16Ω. It shows full scale deflection, when a current of 20 mA is passed through it. The only shunt resistance available is 0.06 which is not appropriate to convert a galvanometer into an ammeter. How much resistance should be connected in series with the coil of galvanometer, so that the range of ammeter is 8 A?
Why is it necessary to introduce a radial magnetic field inside the coil of a galvanometer?
Write current sensitivity of a galvanomete S.I. unit.
A moving coil galvanometer has a coil of resistance 59 Ω. It shows a full-scale deflection for a current of 50 mA. How will you convert it to an ammeter having a range of 0 to 3A?
Explain the significance of a radial magnetic field when a current-carrying coil is kept in it.
The conversion of a moving coil galvanometer into a voltmeter is done by ______.
A galvanometer of resistance 100 Ω gives a full-scale deflection for a current of 10−5 A. To convert it into an ammeter capable of measuring up to 1 A we should connect a resistance of ______.
Explain in brief the basic construction of a moving-coil table galvanometer whit a neat labelled diagram.
