Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A moving coil galvanometer has a coil of resistance 59 Ω. It shows a full-scale deflection for a current of 50 mA. How will you convert it to an ammeter having a range of 0 to 3A?
उत्तर
Let resistance of R, Ω be shunted with galvanometer to make it an ammeter in parallel.
p.d. across the galvanometer = p.d. across the shunt
IC1 x RC1 =(I- lC1 ) . RS
⇒ `R_s = (I_(C_1)R_(C_1))/(I-I_(C_1))=(50xx10^-3 xx59)/((3-50xx10^-3))`
⇒ `R_s = (50xx10^-3 xx59)/2.95 = (50xx10^-3 xx10^2 xx59)/295`
∴ `R_s = 1 Omega `
A resistance of 1 Ω be required to shunt in order to comvert this into ammeter.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A rectangular coil of a moving coil galvanometer contains 50 turns each having area 12 cm2 . It is suspended in radial magnetic field 0.025 Wb/m2 by a fibre of twist constant 15 x10-10 Nm/degree. Calculate the sensitivity of the moving coil galvanometer.
A circular coil of 250 turns and diameter 18 cm carries a current of 12A. What is the magnitude of magnetic moment associated with the coil?
Draw a labelled diagram of a moving coil galvanometer. Describe briefly its principle and working.
A galvanometer has a resistance of 16Ω. It shows full scale deflection, when a current of 20 mA is passed through it. The only shunt resistance available is 0.06 which is not appropriate to convert a galvanometer into an ammeter. How much resistance should be connected in series with the coil of galvanometer, so that the range of ammeter is 8 A?
How will you convert a moving coil galvanometer into a voltmeter?
Write current sensitivity of a galvanomete S.I. unit.
The current sensitivity of a galvanometer increase by 20%. If its resistance also increases by 25%, the voltage sensitivity will ______.
A galvanometer of resistance 100 Ω gives a full-scale deflection for a current of 10−5 A. To convert it into an ammeter capable of measuring up to 1 A we should connect a resistance of ______.
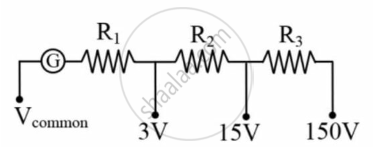
A voltmeter of variable ranges 3 V, 15 V, 150 V is to be designed by connecting resistances R1, R2, R3 in series with a galvanometer of resistance G = 20 Ω, as shown in Fig. The galvanometer gives full pass through its coil for 1 mA current i.e. "gives full pass through it's coil for 1 mA current". Then, the resistances R1, R2 and R3 (in kilo ohms) should be, respectively: