Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
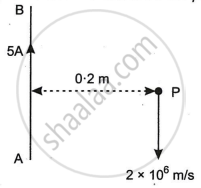
A long straight wire AB carries a current of 5A. P is a proton travelling with a velocity of 2 × 106 m/s, parallel to the wire, 0.2 m from it and in a direction opposite to the current, as shown in Figure below. Calculate the force which magnetic field of the current carrying conductor AB exerts on the proton.
उत्तर
The magnetic field due to the current carrying wire is perpendicular to the plane of the paper, in a downward direction.
i.e., `vec"B" = - (mu_0"I")/(2pi"d") vec"k"`
Force `vec "F" = q vecv xx vec"B"`
`= e(- v vec"j") xx (- (mu_0"I")/(2pi"d") vec"k")`
`= (mu_0ev"I")/(2pi"d") vec "i"`
Given that d = 0.2 m, ν = 2 × 106 m/s, I = 5 A
`therefore "F" = (mu_0"e" xx 2 xx 10^6 xx 5 xx 10^5)/(2pi xx 0.2) vec"i"`
`= (2 xx 10^-7 xx 1.6 xx 10^-19 xx 2 xx 10^6 xx 5 xx 10^5)/0.2`
`= 160 xx 10^-13` N
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Use this law to find magnetic field due to straight infinite current carrying wire.
A long straight wire in the horizontal plane carries a current of 50 A in north to south direction. Give the magnitude and direction of B at a point 2.5 m east of the wire.
Explain the term hysteresis
Define magnetic lines of force
A charged particle is moved along a magnetic field line. The magnetic force on the particle is
Choose the correct alternative and rewrite the following:
What will happen to the current passing through a resistance, if the potential difference across it is doubled and the resistance is halved?
The force between two parallel current-carrying conductors is F. If the current in each conductor is doubled, then the force between them becomes ______
A particle of charge -16 x 10-18 C moving with velocity 10 m/s along the X-axis enters a region where a magnetic field of induction B is along Y-axis and electric field of magnitude 104 V/m is along the negative Z-axis. If the charged particle continues moving along the X-axis, the magnitude of B is ____________.
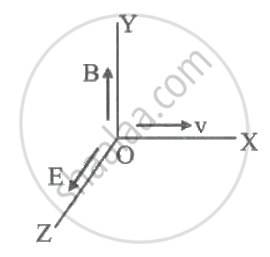
An electron travelling west to east enters a chamber having a uniform electrostatic field in north to south direction. Specify the direction in which a uniform magnetic field should be set up to prevent the electron from deflecting from its straight line path.
In SI system, permeability has the units ______.
In the product
`overset(->)("F") = "q"(overset(->)(υ) xx overset(->)("B"))`
= `"q"overset(->)(υ) xx ("B"overset(^)("i") + "B" overset(^)("j") + "B"_0overset(^)("k"))`
For q = 1 and `overset(->)(υ) = 2overset(^)("i") + 4overset(^)("j") + 6overset(^)("k")` and
`overset(->)("F") = 4overset(^)("i") - 20overset(^)("j") + 12overset(^)("k")`
What will be the complete expression for `overset(->)("B")`?
A circular current loop of magnetic moment M is in an arbitrary orientation in an external magnetic field B. The work done to rotate the loop by 30° about an axis perpendicular to its plane is ______.
Consider a wire carrying a steady current, I placed in a uniform magnetic field B perpendicular to its length. Consider the charges inside the wire. It is known that magnetic forces do no work. This implies that ______.
- motion of charges inside the conductor is unaffected by B since they do not absorb energy.
- some charges inside the wire move to the surface as a result of B.
- if the wire moves under the influence of B, no work is done by the force.
- if the wire moves under the influence of B, no work is done by the magnetic force on the ions, assumed fixed within the wire.
A cubical region of space is filled with some uniform electric and magnetic fields. An electron enters the cube across one of its faces with velocity v and a positron enters via opposite face with velocity – v. At this instant ______.
- the electric forces on both the particles cause identical accelerations.
- the magnetic forces on both the particles cause equal accelerations.
- both particles gain or loose energy at the same rate.
- the motion of the centre of mass (CM) is determined by B alone.
A long straight wire carrying current of 25 A rests on a table as shown in figure. Another wire PQ of length 1 m, mass 2.5 g carries the same current but in the opposite direction. The wire PQ is free to slide up and down. To what height will PQ rise?
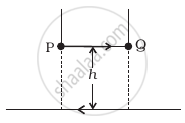
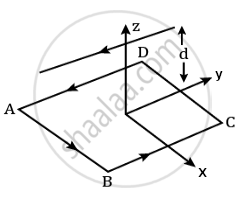
Figure shows a square loop. 20 cm on each side in the x-y plane with its centre at the origin. The loop carries a current of 7 A. Above it at y = 0, z = 12 cm is an infinitely long wire parallel to the x axis carrying a current of 10 A. The net force on the loop is ______ × 10-4 N.
A long straight conductor kept along X' X axis, carries a steady current I along the +x direction. At an instant t, a particle of mass m and charge q at point (x, y) moves with a velocity `vecv` along +y direction. Find the magnitude and direction of the force on the particle due to the conductor.
