Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
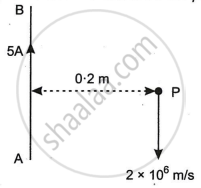
A long straight wire AB carries a current of 5A. P is a proton travelling with a velocity of 2 × 106 m/s, parallel to the wire, 0.2 m from it and in a direction opposite to the current, as shown in Figure below. Calculate the force which magnetic field of the current carrying conductor AB exerts on the proton.
उत्तर
The magnetic field due to the current carrying wire is perpendicular to the plane of the paper, in a downward direction.
i.e., `vec"B" = - (mu_0"I")/(2pi"d") vec"k"`
Force `vec "F" = q vecv xx vec"B"`
`= e(- v vec"j") xx (- (mu_0"I")/(2pi"d") vec"k")`
`= (mu_0ev"I")/(2pi"d") vec "i"`
Given that d = 0.2 m, ν = 2 × 106 m/s, I = 5 A
`therefore "F" = (mu_0"e" xx 2 xx 10^6 xx 5 xx 10^5)/(2pi xx 0.2) vec"i"`
`= (2 xx 10^-7 xx 1.6 xx 10^-19 xx 2 xx 10^6 xx 5 xx 10^5)/0.2`
`= 160 xx 10^-13` N
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Deduce the expression for the magnetic field at a point on the axis of a current carrying circular loop of radius ‘R’ distant ‘x’ from the centre. Hence, write the magnetic field at the centre of a loop.
Magnetic lines of force always cross each other
Obtain an expression for magnetic flux density B at the centre of a circular coil of radius R, having N turns and carrying a current I
A particle of charge ‘q’ and mass ‘m’ is moving with velocity .`vecV` It is subjected to a uniform magnetic field `vecB` directed perpendicular to its velocity. Show that it describes a circular path. Write the expression for its radius.
The net charge in a current-carrying wire is zero. Then, why does a magnetic field exert a force on it?
The force between two parallel current-carrying conductors is F. If the current in each conductor is doubled, then the force between them becomes ______
Show that currents in two long, straight, parallel wires exert forces on each other. Derive the expression for the force per unit length on each conductor.
A particle with charge q moves with a velocity v in a direction perpendicular to the directions of uniform electric and magnetic fields, E and B respectively, which are mutually perpendicular to each other. Which one of the following gives the condition for which the particle moves undeflected in its original trajectory?
Correct unit of magnetic field is ______.
The phenomenon in which a magnetic field is produced in the space near a conductor carrying current is called ______
Two charged particles traverse identical helical paths in a completely opposite sense in a uniform magnetic field B = B0k̂.
Show that a force that does no work must be a velocity dependent force.
Two long current-carrying conductors are placed parallel to each other at a distance of 8 cm between them. The magnitude of the magnetic field produced at the mid-point between the two conductors due to the current flowing in them is 300µT. The equal current flowing in the two conductors is ______.
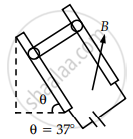
Two conducting rails are connected to a source of emf and form an incline as shown in figure. A bar of mass 50 g slides without friction down the incline through a vertical magnetic field B. If the length of the bar is 50 cm and a current of 2.5 A is provided by battery. Value of B for which the bar slide at a constant velocity ______ × 10-1 Tesla. 2 [g = 10 m/s2]
A unit vector is represented as `(0.8hat"i" + "b"hat"j" + 0.4hat"k")`. Hence the value of 'b' must be ______.
A long straight conductor kept along X' X axis, carries a steady current I along the +x direction. At an instant t, a particle of mass m and charge q at point (x, y) moves with a velocity `vecv` along +y direction. Find the magnitude and direction of the force on the particle due to the conductor.
With a neat labelled diagram, explain cyclotron motion and cyclotron formula.
