Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The force between two parallel current-carrying conductors is F. If the current in each conductor is doubled, then the force between them becomes ______
विकल्प
4F
2F
F
F/4
उत्तर
The force between two parallel current-carrying conductors is F. If the current in each conductor is doubled, then the force between them becomes 4F.
संबंधित प्रश्न
Use this law to find magnetic field due to straight infinite current carrying wire.
Deduce the expression for the magnetic field at a point on the axis of a current carrying circular loop of radius ‘R’ distant ‘x’ from the centre. Hence, write the magnetic field at the centre of a loop.
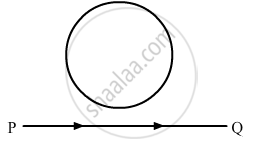
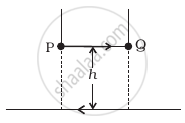
A conducting loop is held above a current carrying wire PQ as shown in the figure. Depict the direction of the current induced in the loop when the current in the wire PQ is constantly increasing.
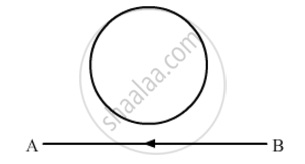
The electric current flowing in a wire in the direction from B to A is decreasing. Find out the direction of the induced current in the metallic loop kept above the wire as shown.
A circular coil of N turns and radius R carries a current I. It is unwound and rewound to make another coil of radius R/2, current I remaining the same. Calculate the ratio of the magnetic moments of the new coil and original coil.
A particle of charge ‘q’ and mass ‘m’ is moving with velocity .`vecV` It is subjected to a uniform magnetic field `vecB` directed perpendicular to its velocity. Show that it describes a circular path. Write the expression for its radius.
The net charge in a current-carrying wire is zero. Then, why does a magnetic field exert a force on it?
A straight wire carrying an electric current is placed along the axis of a uniformly charged ring. Will there be a magnetic force on the wire if the ring starts rotating about the wire? If yes, in which direction?
Two wires carrying equal currents i each, are placed perpendicular to each other, just avoiding a contact. If one wire is held fixed and the other is free to move under magnetic forces, what kind of motion will result?
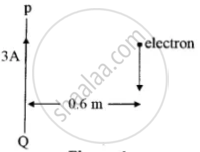
PQ is a long straight conductor carrying a current of 3A as shown in Figure below. An electron moves with a velocity of 2 x 107 ms-1 parallel to it. Find the force acting on the electron.
Explain "Magnetic force never does any work on moving charges".
Show that currents in two long, straight, parallel wires exert forces on each other. Derive the expression for the force per unit length on each conductor.
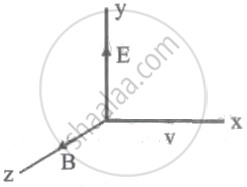
A particle with charge q moves with a velocity v in a direction perpendicular to the directions of uniform electric and magnetic fields, E and B respectively, which are mutually perpendicular to each other. Which one of the following gives the condition for which the particle moves undeflected in its original trajectory?
A magnetic field set up using Helmholtz coils is uniform in a small region and has a magnitude of 0.75 T. In the same region, a uniform electrostatic field is maintained in a direction normal to the common axis of the coils. A narrow beam of (single species) charged particles all accelerated through 15 kV enters this region in a direction perpendicular to both the axis of the coils and the electrostatic field. If the beam remains undeflected when the electrostatic field is 9.0 × 10–5 V m–1, make a simple guess as to what the beam contains. Why is the answer not unique?
A solenoid 60 cm long and of radius 4.0 cm has 3 layers of windings of 300 turns each. A 2.0 cm long wire of mass 2.5 g lies inside the solenoid (near its centre) normal to its axis; both the wire and the axis of the solenoid are in the horizontal plane. The wire is connected through two leads parallel to the axis of the solenoid to an external battery which supplies a current of 6.0 A in the wire. What value of current (with appropriate sense of circulation) in the windings of the solenoid can support the weight of the wire? (g = 9.8 m s–2)
- If v is parallel to B, then path of particle is spiral.
- If v is perpendicular to B, then path of particle is a circle.
- If v has a component along B, then path of particle is helical.
- If v is along B, then path of particle is a circle.
The magnetic moment of a current I carrying circular coil of radius r and number of turns N varies as ______.
A magnetic field exerts no force on
A circular current loop of magnetic moment M is in an arbitrary orientation in an external magnetic field B. The work done to rotate the loop by 30° about an axis perpendicular to its plane is ______.
A long straight wire carrying current of 25 A rests on a table as shown in figure. Another wire PQ of length 1 m, mass 2.5 g carries the same current but in the opposite direction. The wire PQ is free to slide up and down. To what height will PQ rise?
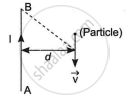
A long straight wire AB carries a current I. A particle (mass m and charge q) moves with a velocity `vec"v"`, parallel to the wire, at a distance d from it as shown in the figure. Obtain the expression for the force experienced by the particle and mention its directions.
With a neat labelled diagram, explain cyclotron motion and cyclotron formula.
What is the relation between Tesla and Gauss?
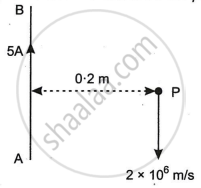
A long straight wire AB carries a current of 5A. P is a proton travelling with a velocity of 2 × 106 m/s, parallel to the wire, 0.2 m from it and in a direction opposite to the current, as shown in Figure below. Calculate the force which magnetic field of the current carrying conductor AB exerts on the proton.
Lorentz force in vector form is ______.
