Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A circular current loop of magnetic moment M is in an arbitrary orientation in an external magnetic field B. The work done to rotate the loop by 30° about an axis perpendicular to its plane is ______.
विकल्प
`MB`.
`sqrt(3) (MB)/2`.
`(MB)/2`.
zero.
उत्तर
A circular current loop of magnetic moment M is in an arbitrary orientation in an external magnetic field B. The work done to rotate the loop by 30° about an axis perpendicular to its plane is zero.
Explanation:
As per the diagram, the rotation of the loop by 30° about an axis perpendicular to its plane makes no variation in the angle made by axis of the loop with the direction of magnetic field, i.e.
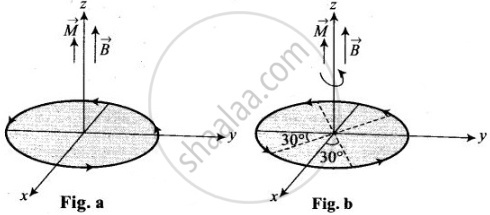
Therefore, the work done to rotate the loop is given by,
W = MB(cos θ1 − cos θ2)
Hence,
W = MB(cos α − cos α) = 0
Work done to rotate the loop is zero.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A circular coil of wire consisting of 100 turns, each of radius 8.0 cm carries a current of 0.40 A. What is the magnitude of the magnetic field B at the centre of the coil?
A straight wire carrying an electric current is placed along the axis of a uniformly charged ring. Will there be a magnetic force on the wire if the ring starts rotating about the wire? If yes, in which direction?
An electron emitted by a heated cathode and accelerated through a potential difference of 2.0 kV, enters a region with uniform magnetic field of 0.15 T. Determine the trajectory of the electron if the field (a) is transverse to its initial velocity, (b) makes an angle of 30° with the initial velocity.
In the product
`overset(->)("F") = "q"(overset(->)(υ) xx overset(->)("B"))`
= `"q"overset(->)(υ) xx ("B"overset(^)("i") + "B" overset(^)("j") + "B"_0overset(^)("k"))`
For q = 1 and `overset(->)(υ) = 2overset(^)("i") + 4overset(^)("j") + 6overset(^)("k")` and
`overset(->)("F") = 4overset(^)("i") - 20overset(^)("j") + 12overset(^)("k")`
What will be the complete expression for `overset(->)("B")`?
A cubical region of space is filled with some uniform electric and magnetic fields. An electron enters the cube across one of its faces with velocity v and a positron enters via opposite face with velocity – v. At this instant ______.
- the electric forces on both the particles cause identical accelerations.
- the magnetic forces on both the particles cause equal accelerations.
- both particles gain or loose energy at the same rate.
- the motion of the centre of mass (CM) is determined by B alone.
Two long current-carrying conductors are placed parallel to each other at a distance of 8 cm between them. The magnitude of the magnetic field produced at the mid-point between the two conductors due to the current flowing in them is 300µT. The equal current flowing in the two conductors is ______.
Two conducting rails are connected to a source of emf and form an incline as shown in figure. A bar of mass 50 g slides without friction down the incline through a vertical magnetic field B. If the length of the bar is 50 cm and a current of 2.5 A is provided by battery. Value of B for which the bar slide at a constant velocity ______ × 10-1 Tesla. 2 [g = 10 m/s2]
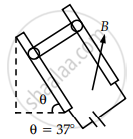
Figure shows a square loop. 20 cm on each side in the x-y plane with its centre at the origin. The loop carries a current of 7 A. Above it at y = 0, z = 12 cm is an infinitely long wire parallel to the x axis carrying a current of 10 A. The net force on the loop is ______ × 10-4 N.
With a neat labelled diagram, explain cyclotron motion and cyclotron formula.
Two long parallel current-carrying conductors are 0.4 m apart in air and carry currents 5 A and 10 A. Calculate the force per metre on each conductor, if the currents are (a) in the same direction and (b) in the opposite direction.
