Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Lorentz force in vector form is ______.
विकल्प
F = Bq v sin θ
`overset(→)(F) = q(overset(→)(v) xx overset(→)(B))`
`overset(→)(F) = q(overset(→)(B) xx overset(→)(v))`
`overset(→)(F) = overset(→)(v)(overset(→)(q) xx overset(→)(B))`
उत्तर
Lorentz force in vector form is `bbunderline(overset(→)(F) = q(overset(→)(v) xx overset(→)(B)))`.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Two long, straight, parallel conductors carry steady currents, I1 and I2, separated by a distance d. If the currents are flowing in the same direction, show how the magnetic field set up in one produces an attractive force on the other? Obtain the expression for this force. Hence, define one ampere.
Use this law to find magnetic field due to straight infinite current carrying wire.
Seema’s uncle was advised by his doctor to have an MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) scan of his brain. Her uncle felt it to be expensive and wanted to postpone it. When Seema learnt about this, she took the help of her family and also approached the doctor, who also offered a substantial discount. She then convinced her uncle to undergo the test to enable the doctor to know the condition of his brain. The information thus obtained greatly helped the doctor to treat him properly.
Based on the above paragraph, answer the following questions:
(a) What according to you are the values displayed by Seema, her family and the doctor?
(b) What could be the possible reason for MRI test to be so expensive?
(c) Assuming that MRI test was performed using a magnetic field of 0.1 T, find the minimum and maximum values of the force that the magnetic field could exert on a proton (charge = 1.6 x 10-19 C) moving with a speed of 104 m/s.
A circular coil of wire consisting of 100 turns, each of radius 8.0 cm carries a current of 0.40 A. What is the magnitude of the magnetic field B at the centre of the coil?
Explain the term hysteresis
The free electrons in a conducting wire are in constant thermal motion. If such a wire, carrying no current, is placed in a magnetic field, is there a magnetic force on each free electron? Is there a magnetic force on the wire?
Which of the following particles will experience maximum magnetic force (magnitude) when projected with the same velocity perpendicular to a magnetic field?
Two wires carrying equal currents i each, are placed perpendicular to each other, just avoiding a contact. If one wire is held fixed and the other is free to move under magnetic forces, what kind of motion will result?
State whether the following statement is true or false:
Magnetic poles exist in pairs.
A particle of charge -16 x 10-18 C moving with velocity 10 m/s along the X-axis enters a region where a magnetic field of induction B is along Y-axis and electric field of magnitude 104 V/m is along the negative Z-axis. If the charged particle continues moving along the X-axis, the magnitude of B is ____________.
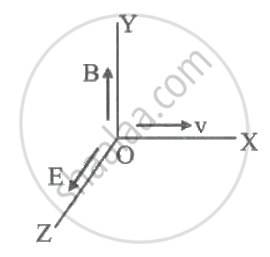
A very high magnetic field is applied to a stationary charge. Then the charge experiences ______.
A charged particle enters an environment of a strong and non-uniform magnetic field varying from point to point both in magnitude and direction, and comes out of it following a complicated trajectory. Would its final speed equal the initial speed if it suffered no collisions with the environment?
Lorentz Force generally refers to ______.
Assertion: Free electrons always keep on moving in a conductor even then no magnetic force act on them in magnetic field unless a current is passed through it.
Reason: The average velocity of free electron is zero.
The magnetic force depends on v which depends on the inertial frame of reference. Does then the magnetic force differ from inertial frame to frame? Is it reasonable that the net acceleration has a different value in different frames of reference?
Figure shows a square loop. 20 cm on each side in the x-y plane with its centre at the origin. The loop carries a current of 7 A. Above it at y = 0, z = 12 cm is an infinitely long wire parallel to the x axis carrying a current of 10 A. The net force on the loop is ______ × 10-4 N.
A unit vector is represented as `(0.8hat"i" + "b"hat"j" + 0.4hat"k")`. Hence the value of 'b' must be ______.
A long straight conductor kept along X' X axis, carries a steady current I along the +x direction. At an instant t, a particle of mass m and charge q at point (x, y) moves with a velocity `vecv` along +y direction. Find the magnitude and direction of the force on the particle due to the conductor.
What is the relation between Tesla and Gauss?
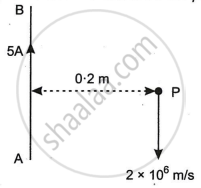
A long straight wire AB carries a current of 5A. P is a proton travelling with a velocity of 2 × 106 m/s, parallel to the wire, 0.2 m from it and in a direction opposite to the current, as shown in Figure below. Calculate the force which magnetic field of the current carrying conductor AB exerts on the proton.