Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
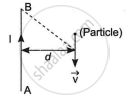
A long straight wire AB carries a current I. A particle (mass m and charge q) moves with a velocity `vec"v"`, parallel to the wire, at a distance d from it as shown in the figure. Obtain the expression for the force experienced by the particle and mention its directions.
उत्तर
Magnetic field induction at P due to current I in long straight wire AB is
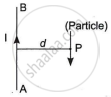
`B = mu_0/(4pi) (2I)/d`
It acts perpendicular to the plane of the paper inward, represented by `hatn`.
Lorentz force acting on the particle at P can be given by
`vecF = q(vecv xx vecB) = e(vecv xx (mu_0. 2I)/(4pid)hatn)`
or `vecF = (mu_0Iev)/(2pid)(hatv xx hatn)`
∴ `F = (mu_0Iev)/(2pid)`
Acting in the plane of paper away from the wire.
संबंधित प्रश्न
Obtain an expression for magnetic flux density B at the centre of a circular coil of radius R, having N turns and carrying a current I
A particle of charge ‘q’ and mass ‘m’ is moving with velocity .`vecV` It is subjected to a uniform magnetic field `vecB` directed perpendicular to its velocity. Show that it describes a circular path. Write the expression for its radius.
The free electrons in a conducting wire are in constant thermal motion. If such a wire, carrying no current, is placed in a magnetic field, is there a magnetic force on each free electron? Is there a magnetic force on the wire?
A straight wire carrying an electric current is placed along the axis of a uniformly charged ring. Will there be a magnetic force on the wire if the ring starts rotating about the wire? If yes, in which direction?
Write the expression for the Lorentz force F in vector form.
Correct unit of magnetic field is ______.
- perpendicular to direction of velocity of charged particle.
-
perpendicular to direction of magnetic field.
-
parallel to direction of velocity of charged particle.
-
parallel to the direction of magnetic field.
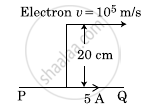
An infinitely long straight conductor carries a current of 5 A as shown. An electron is moving with a speed of 105 m/s parallel to the conductor. The perpendicular distance between the electron and the conductor is 20 cm at an instant. Calculate the magnitude of the force experienced by the electron at that instant.
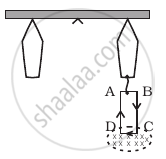
A 100 turn rectangular coil ABCD (in XY plane) is hung from one arm of a balance (Figure). A mass 500 g is added to the other arm to balance the weight of the coil. A current 4.9 A passes through the coil and a constant magnetic field of 0.2 T acting inward (in xz plane) is switched on such that only arm CD of length 1 cm lies in the field. How much additional mass ‘m’ must be added to regain the balance?
Distinguish between the forces experienced by a moving charge in a uniform electric field and in a uniform magnetic field. (Any two points)
