Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A moving coil galvanometer of resistance 55 Ω produces a full scale deflection for a current of 250 mA. How will you convert it into an ammeter with a range of 0 - 3A?
उत्तर
Galvanometer - Ammeter
and shunt is parallel to galvanometer
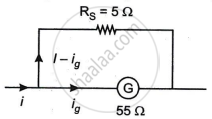
Rs(I - ig) = igG
`"R"_"s" = (250 xx 10^-3 xx 55)/(3 - 250 xx 10^-3)`
`"R"_"s" = 13.75/2.75`
Rs = 5 Ω
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
An ideal voltmeter has _______.
(A) low resistance
(b) high resistance
(C) infinite resistance
(D) zero resistance
Define the current sensitivity of a galvanometer ?
Explain, giving reasons, the basic difference in converting a galvanometer into (i) a voltmeter and (ii) an ammeter?
Draw a labelled diagram of a moving coil galvanometer and explain its working. What is the function of radial magnetic field inside the coil?
The coil of a moving coil galvanometer is wound over a metal frame in order to ______.
A galvanometer of resistance 100 Ω gives a full-scale deflection for a current of 10−5 A. To convert it into an ammeter capable of measuring up to 1 A we should connect a resistance of ______.
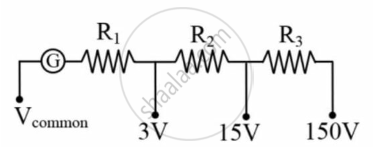
A voltmeter of variable ranges 3 V, 15 V, 150 V is to be designed by connecting resistances R1, R2, R3 in series with a galvanometer of resistance G = 20 Ω, as shown in Fig. The galvanometer gives full pass through its coil for 1 mA current i.e. "gives full pass through it's coil for 1 mA current". Then, the resistances R1, R2 and R3 (in kilo ohms) should be, respectively:
When a galvanometer is shunted with a 4 Ω resistance, the deflection is reduced to one-fifth. If the galvanometer is further shunted with a 2 Ω wire. The further reduction (find the ratio of decrease in current to the previous current) in the deflection will be (the main current remains the same)
How is current sensitivity increased?
