Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain, giving reasons, the basic difference in converting a galvanometer into (i) a voltmeter and (ii) an ammeter?
उत्तर
(i) In converting a galvanometer into a voltmeter, a very high suitable resistance is connected is series to its coil. So, the galvanometer gives full scale deflection.
(ii) In converting a galvanometer into an ammeter, a very small suitable resistance is connected in parallel to its coil. The remaining pair of the current i.e. (I − Ig) flows through the resistance. Here I = Circuit current
Ig = Current through galvanometer
संबंधित प्रश्न
Obtain the expression for current sensitivity of moving coil galvanometer.
- A circular coil of 30 turns and radius 8.0 cm carrying a current of 6.0 A is suspended vertically in a uniform horizontal magnetic field of magnitude 1.0 T. The field lines make an angle of 60° with the normal of the coil. Calculate the magnitude of the counter torque that must be applied to prevent the coil from turning.
- Would your answer change, if the circular coil in (a) were replaced by a planar coil of some irregular shape that encloses the same area? (All other particulars are also unaltered.)
State how a moving coil galvanometer can be converted into an ammeter.
The AC voltage across a resistance can be measured using a ______.
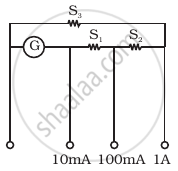
A multirange voltmeter can be constructed by using a galvanometer circuit as shown in figure. We want to construct a voltmeter that can measure 2V, 20V and 200V using a galvanometer of resistance 10Ω and that produces maximum deflection for current of 1 mA. Find R1, R2 and R3 that have to be used.
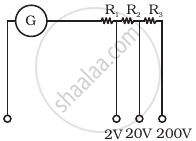
A multirange current meter can be constructed by using a galvanometer circuit as shown in figure. We want a current meter that can measure 10 mA, 100 mA and 1A using a galvanometer of resistance 10 Ω and that prduces maximum deflection for current of 1mA. Find S1, S2 and S3 that have to be used
A voltmeter has a range of 0 - 20 V and a resistance of 500 Q. Explain how can be used to measure voltages from 0 - 200 volt?
Assertion: When an electric current is passed through a moving coil galvanometer, its coil gets deflected.
Reason: A circular coil produces a uniform magnetic field around itself when an electric current is passed through it.
