Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
- A circular coil of 30 turns and radius 8.0 cm carrying a current of 6.0 A is suspended vertically in a uniform horizontal magnetic field of magnitude 1.0 T. The field lines make an angle of 60° with the normal of the coil. Calculate the magnitude of the counter torque that must be applied to prevent the coil from turning.
- Would your answer change, if the circular coil in (a) were replaced by a planar coil of some irregular shape that encloses the same area? (All other particulars are also unaltered.)
उत्तर
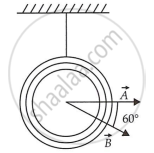
- Number of turns on the circular coil, n = 30
Radius of the coil, r = 8.0 cm = 0.08 m
Area of the coil = πr2 = π(0.08)2 = 0.0201 m2
Current flowing in the coil, I = 6.0 A
Magnetic field strength, B = 1 T
Angle between the field lines and normal with the coil surface,
θ = 60°
The coil experiences a torque in the magnetic field. Hence, it turns. The counter torque applied to prevent the coil from turning is given by the relation,
τ = n IBA sin θ …........(i)
= 30 × 6 × 1 × 0.0201 × sin 60°
= 3.133 N m - It can be inferred from the relation (i) that the magnitude of the applied torque is not dependent on the shape of the coil. It depends on the area of the coil. Hence, the answer would not change if the circular coil in the above case is replaced by a planar coil of some irregular shape that encloses the same area.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A rectangular coil of a moving coil galvanometer contains 50 turns each having area 12 cm2 . It is suspended in radial magnetic field 0.025 Wb/m2 by a fibre of twist constant 15 x10-10 Nm/degree. Calculate the sensitivity of the moving coil galvanometer.
Show that the current flowing through a moving coil galvanometer is directly proportional to the angle of deflection of coil.
Write the underlying principle of a moving coil galvanometer.
A galvanometer of resistance G is converted into a voltmeter to measure upto V volts by connecting a resistance R1 in series with the coil. If a resistance R2 is connected in series with it, then it can measures upto V/2 volts. Find the resistance, in terms of R1 and R2, required to be connected to convert it into a voltmeter that can read upto 2 V. Also find the resistance G of the galvanometer in terms of R1 and R2
Increasing the current sensitivity of a galvanometer may not necessarily increase its voltage sensitivity. Explain, giving reason.
State the underlying principle of working of a moving coil galvanometer. Write two reasons why a galvanometer can not be used as such to measure current in a given circuit. Name any two factors on which the current sensitivity of a galvanometer depends.
What are the advantages of using soft iron as a core, instead of steel, in the coils of galvanometers?
A moving coil galvanometer has a coil of resistance 59 Ω. It shows a full-scale deflection for a current of 50 mA. How will you convert it to an ammeter having a range of 0 to 3A?
The deflection in a moving coil galvanometer is ______.
The current sensitivity of a galvanometer increase by 20%. If its resistance also increases by 25%, the voltage sensitivity will ______.
A galvanometer of resistance 100 Ω gives a full-scale deflection for a current of 10−5 A. To convert it into an ammeter capable of measuring up to 1 A we should connect a resistance of ______.
A galvanometer having a coil resistance of 60 Ω shows full-scale deflection when a current of 1.0 amp passes through it. It can be converted into an ammeter to read currents up to 5.0 amp by:
A galvanometer coil bas 500 turns and each tum has an average area of 3 × 10-4 m2. If a torque of 1.5 Nm is required to keep this coil parallel to a magnetic field when a current of 0.5 A is flowing through it, the strength of the field (in T) is ______.
A galvanometer having a resistance of 20 Ω and 30 Ω division on both sides has figure of merit 0.005 ampere/division. The resistance that should be connected in series such that it can be used as a voltmeter upto 15 volt, is ______.
How is current sensitivity increased?
A moving coil galvanometer of resistance 55 Ω produces a full scale deflection for a current of 250 mA. How will you convert it into an ammeter with a range of 0 - 3A?
The figure below shows a circuit containing an ammeter A, a galvanometer G and a plug key K. When the key is closed: