Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The figure below shows a circuit containing an ammeter A, a galvanometer G and a plug key K. When the key is closed:
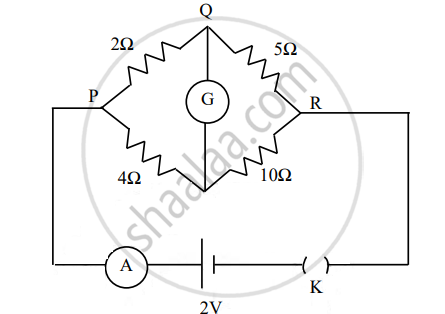
विकल्प
both G and A show deflections.
neither G nor A shows deflection.
G shows deflection but A does not.
A shows deflection but G does not.
उत्तर
A shows deflection but G does not.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The combined resistance of a galvanometer of resistance 500Ω and its shunt is 21Ω. Calculate the value of shunt.
The combined resistance of a galvanometer of resistance 500Ω and its shunt is 21Ω. Calculate the value of shunt.
Write the underlying principle of a moving coil galvanometer.
A galvanometer of resistance G is converted into a voltmeter to measure upto V volts by connecting a resistance R1 in series with the coil. If a resistance R2 is connected in series with it, then it can measures upto V/2 volts. Find the resistance, in terms of R1 and R2, required to be connected to convert it into a voltmeter that can read upto 2 V. Also find the resistance G of the galvanometer in terms of R1 and R2
Why is it necessary to introduce a cylindrical soft iron core inside the coil of a galvanometer?
Write current sensitivity of a galvanomete S.I. unit.
In a moving coil galvanometer the deflection (Φ) on the scale by a pointer attached to the spring is ______.
A galvanometer having a coil resistance of 60 Ω shows full-scale deflection when a current of 1.0 amp passes through it. It can be converted into an ammeter to read currents up to 5.0 amp by:
When a galvanometer is shunted with a 4 Ω resistance, the deflection is reduced to one-fifth. If the galvanometer is further shunted with a 2 Ω wire. The further reduction (find the ratio of decrease in current to the previous current) in the deflection will be (the main current remains the same)
To convert a moving coil galvanometer into an ammeter we need to connect a ______.
