Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A multirange voltmeter can be constructed by using a galvanometer circuit as shown in figure. We want to construct a voltmeter that can measure 2V, 20V and 200V using a galvanometer of resistance 10Ω and that produces maximum deflection for current of 1 mA. Find R1, R2 and R3 that have to be used.
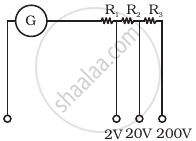
उत्तर
The galvanometer can also be used as a voltmeter to measure the voltage across a given section of the circuit. For this, a very high resistance wire is to be connected in series with galvanometer. The relationship is given by Ig (G + R) – V where Ig is the range of galvanometer, G is the resistance of galvanometer and R is the resistance of wire connected in series with galvanometer.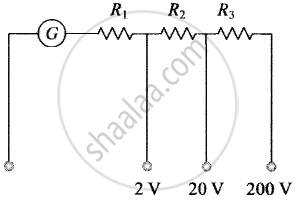
Applying expression in different situations
For `i_G (G + R_1)` = 2 for 2 V range
For `i_G (G + R_1 + R_2)` = 20 for 20 V range
And For `i_G (G + R_1 + R_2 + R_3)` = 200 for 200 V range
By solving, we get
R1 = 1990 Ω R2 = 18 kΩ and R3 = 180 kΩ.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Two moving coil meters, M1 and M2 have the following particulars:
R1 = 10 Ω, N1 = 30,
A1 = 3.6 × 10–3 m2, B1 = 0.25 T
R2 = 14 Ω, N2 = 42,
A2 = 1.8 × 10–3 m2, B2 = 0.50 T
(The spring constants are identical for the two meters).
Determine the ratio of
- current sensitivity and
- voltage sensitivity of M2 and M1.
- A circular coil of 30 turns and radius 8.0 cm carrying a current of 6.0 A is suspended vertically in a uniform horizontal magnetic field of magnitude 1.0 T. The field lines make an angle of 60° with the normal of the coil. Calculate the magnitude of the counter torque that must be applied to prevent the coil from turning.
- Would your answer change, if the circular coil in (a) were replaced by a planar coil of some irregular shape that encloses the same area? (All other particulars are also unaltered.)
A moving coil galvanometer has a resistance of 25Ω and gives a full scale deflection for a current of 10mA. How will you convert it into a voltmeter having range 0 - 100 V?
Why is it necessary to introduce a radial magnetic field inside the coil of a galvanometer?
Define the current sensitivity of a galvanometer ?
State the underlying principle of working of a moving coil galvanometer. Write two reasons why a galvanometer can not be used as such to measure current in a given circuit. Name any two factors on which the current sensitivity of a galvanometer depends.
State how a moving coil galvanometer can be converted into an ammeter.
The AC voltage across a resistance can be measured using a ______.
Explain in brief the basic construction of a moving-coil table galvanometer whit a neat labelled diagram.
A moving coil galvanometer of resistance 55 Ω produces a full scale deflection for a current of 250 mA. How will you convert it into an ammeter with a range of 0 - 3A?
