Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Two moving coil meters, M1 and M2 have the following particulars:
R1 = 10 Ω, N1 = 30,
A1 = 3.6 × 10–3 m2, B1 = 0.25 T
R2 = 14 Ω, N2 = 42,
A2 = 1.8 × 10–3 m2, B2 = 0.50 T
(The spring constants are identical for the two meters).
Determine the ratio of
- current sensitivity and
- voltage sensitivity of M2 and M1.
उत्तर
For moving coil meter M1:
Resistance, R1 = 10 Ω
Number of turns, N1 = 30
Area of cross-section, A1 = 3.6 × 10–3 m2
Magnetic field strength, B1 = 0.25 T
Spring constant K1 = K
For moving coil meter M2:
Resistance, R2 = 14 Ω
Number of turns, N2 = 42
Area of cross-section, A2 = 1.8 × 10–3 m2
Magnetic field strength, B2 = 0.50 T
Spring constant, K2 = K
(a) Current sensitivity of M1 is given as:
`"I"_("s"_1) = ("N"_1"B"_1"A"_1)/"K"_1`
And, current sensitivity of M2 is given as:
`"I"_("s"_2) = ("N"_2"B"_2"A"_2)/"K"_2`
∴ Ratio `"I"_("s"_2)/"I"_("s"_1) = ("N"_2"B"_2"A"_2"K"_1)/("N"_1"B"_1"A"_1"K"_2)`
= `(42 xx 0.5 xx 1.8 xx 10^-3 xx "K")/(30 xx 0.25 xx 3.6 xx 10^-3 xx "K")`
= 1.4
Hence, the ratio of current sensitivity of M2 to M1 is 1.4.
(b) Voltage sensitivity for M2 is given as:
`"V"_("s"_2) = ("N"_2"B"_2"A"_2)/("K"_2"R"_2)`
And, voltage sensitivity for M1 is given as:
`"V"_("s"_1) = ("N"_1"B"_1"A"_1)/("K"_1"R"_1)`
∴ Ratio `"V"_("s"_2)/"V"_("s"_1) = ("N"_2"B"_2"A"_2"K"_1"R"_1)/("N"_1"B"_1"A"_1"K"_2"R"_2)`
= `(42 xx 0.5 xx 1.8 xx 10^-3 xx "K" xx 10)/(30 xx 0.25 xx 3.6 xx 10^-3 xx "K" xx 14)`
= 1
Hence, the ratio of voltage sensitivity of M2 to M1 is 1.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A rectangular coil of a moving coil galvanometer contains 50 turns each having area 12 cm2 . It is suspended in radial magnetic field 0.025 Wb/m2 by a fibre of twist constant 15 x10-10 Nm/degree. Calculate the sensitivity of the moving coil galvanometer.
Show that the current flowing through a moving coil galvanometer is directly proportional to the angle of deflection of coil.
An ideal voltmeter has _______.
(A) low resistance
(b) high resistance
(C) infinite resistance
(D) zero resistance
- A circular coil of 30 turns and radius 8.0 cm carrying a current of 6.0 A is suspended vertically in a uniform horizontal magnetic field of magnitude 1.0 T. The field lines make an angle of 60° with the normal of the coil. Calculate the magnitude of the counter torque that must be applied to prevent the coil from turning.
- Would your answer change, if the circular coil in (a) were replaced by a planar coil of some irregular shape that encloses the same area? (All other particulars are also unaltered.)
Explain how moving coil galvanometer is converted into a voltmeter. Derive the necessary formula.
A rectangular coil of a moving coil galvanometer contains 100 turns, each having area
15 cm2. It is suspended in the radial magnetic field 0.03 T. The twist constant of suspension
fibre is 15 x 10-10 N-m/degree. Calculate the sensitivity of the moving coil galvanometer.
A moving coil galvanometer has a resistance of 25Ω and gives a full scale deflection for a current of 10mA. How will you convert it into a voltmeter having range 0 - 100 V?
Explain, giving reasons, the basic difference in converting a galvanometer into (i) a voltmeter and (ii) an ammeter?
Draw a labelled diagram of a moving coil galvanometer and explain its working. What is the function of radial magnetic field inside the coil?
A coil of radius 10 cm and resistance 40 Ω has 1000 turns. It is placed with its plane vertical and its axis parallel to the magnetic meridian. The coil is connected to a galvanometer and is rotated about the vertical diameter through an angle of 180°. Find the charge which flows through the galvanometer if the horizontal component of the earth's magnetic field is BH = 3.0 × 10−5 T.
A galvanometer coil has a resistance of 15 Ω and the metre shows full scale deflection for a current of 4 mA. How will you convert the metre into an ammeter of range 0 to 6 A?
A moving coil galvanometer can be converted into an ammeter by ______.
The conversion of a moving coil galvanometer into a voltmeter is done by ______.
The coil of a moving coil galvanometer is wound over a metal frame in order to ______.
A galvanometer of resistance 100 Ω gives a full-scale deflection for a current of 10−5 A. To convert it into an ammeter capable of measuring up to 1 A we should connect a resistance of ______.
The coil of galvanometer consists of 100 turns and effective area of 1 square cm. The restoring couple is 10-8 N-m/rad. The magnetic field between the pole pieces is 5T. The current sensitivity of this galvanometer will be ______.
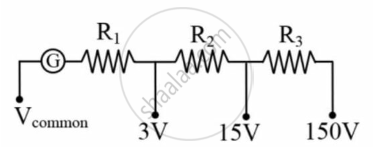
A voltmeter of variable ranges 3 V, 15 V, 150 V is to be designed by connecting resistances R1, R2, R3 in series with a galvanometer of resistance G = 20 Ω, as shown in Fig. The galvanometer gives full pass through its coil for 1 mA current i.e. "gives full pass through it's coil for 1 mA current". Then, the resistances R1, R2 and R3 (in kilo ohms) should be, respectively:
How is current sensitivity increased?
Explain in brief the basic construction of a moving-coil table galvanometer whit a neat labelled diagram.
