Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Two moving coil meters, M1 and M2 have the following particulars:
R1 = 10 Ω, N1 = 30,
A1 = 3.6 × 10–3 m2, B1 = 0.25 T
R2 = 14 Ω, N2 = 42,
A2 = 1.8 × 10–3 m2, B2 = 0.50 T
(The spring constants are identical for the two meters).
Determine the ratio of
- current sensitivity and
- voltage sensitivity of M2 and M1.
Solution
For moving coil meter M1:
Resistance, R1 = 10 Ω
Number of turns, N1 = 30
Area of cross-section, A1 = 3.6 × 10–3 m2
Magnetic field strength, B1 = 0.25 T
Spring constant K1 = K
For moving coil meter M2:
Resistance, R2 = 14 Ω
Number of turns, N2 = 42
Area of cross-section, A2 = 1.8 × 10–3 m2
Magnetic field strength, B2 = 0.50 T
Spring constant, K2 = K
(a) Current sensitivity of M1 is given as:
`"I"_("s"_1) = ("N"_1"B"_1"A"_1)/"K"_1`
And, current sensitivity of M2 is given as:
`"I"_("s"_2) = ("N"_2"B"_2"A"_2)/"K"_2`
∴ Ratio `"I"_("s"_2)/"I"_("s"_1) = ("N"_2"B"_2"A"_2"K"_1)/("N"_1"B"_1"A"_1"K"_2)`
= `(42 xx 0.5 xx 1.8 xx 10^-3 xx "K")/(30 xx 0.25 xx 3.6 xx 10^-3 xx "K")`
= 1.4
Hence, the ratio of current sensitivity of M2 to M1 is 1.4.
(b) Voltage sensitivity for M2 is given as:
`"V"_("s"_2) = ("N"_2"B"_2"A"_2)/("K"_2"R"_2)`
And, voltage sensitivity for M1 is given as:
`"V"_("s"_1) = ("N"_1"B"_1"A"_1)/("K"_1"R"_1)`
∴ Ratio `"V"_("s"_2)/"V"_("s"_1) = ("N"_2"B"_2"A"_2"K"_1"R"_1)/("N"_1"B"_1"A"_1"K"_2"R"_2)`
= `(42 xx 0.5 xx 1.8 xx 10^-3 xx "K" xx 10)/(30 xx 0.25 xx 3.6 xx 10^-3 xx "K" xx 14)`
= 1
Hence, the ratio of voltage sensitivity of M2 to M1 is 1.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A galvanometer of resistance G is converted into a voltmeter to measure upto V volts by connecting a resistance R1 in series with the coil. If a resistance R2 is connected in series with it, then it can measures upto V/2 volts. Find the resistance, in terms of R1 and R2, required to be connected to convert it into a voltmeter that can read upto 2 V. Also find the resistance G of the galvanometer in terms of R1 and R2
Why is it necessary to introduce a cylindrical soft iron core inside the coil of a galvanometer?
The fraction of the total current passing through the galvanometer is ............ .
a) `S/(S+G)`
b) `G/(S+G)`
c) `(S+G)/G`
d) `(S+G)/S`
Draw a labelled diagram of a moving coil galvanometer and explain its working. What is the function of radial magnetic field inside the coil?
State the principle of the working of a moving coil galvanometer, giving its labeled diagram ?
A moving coil galvanometer has a coil of resistance 59 Ω. It shows a full-scale deflection for a current of 50 mA. How will you convert it to an ammeter having a range of 0 to 3A?
State how a moving coil galvanometer can be converted into an ammeter.
Define the term 'current sensitivity' of a moving coil galvanometer.
The deflection in a moving coil galvanometer is ______.
A moving coil galvanometer can be converted into an ammeter by ______.
A galvanometer having a coil resistance of 60 Ω shows full-scale deflection when a current of 1.0 amp passes through it. It can be converted into an ammeter to read currents up to 5.0 amp by:
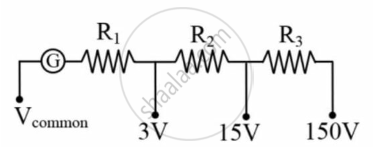
A voltmeter of variable ranges 3 V, 15 V, 150 V is to be designed by connecting resistances R1, R2, R3 in series with a galvanometer of resistance G = 20 Ω, as shown in Fig. The galvanometer gives full pass through its coil for 1 mA current i.e. "gives full pass through it's coil for 1 mA current". Then, the resistances R1, R2 and R3 (in kilo ohms) should be, respectively:
When a galvanometer is shunted with a 4 Ω resistance, the deflection is reduced to one-fifth. If the galvanometer is further shunted with a 2 Ω wire. The further reduction (find the ratio of decrease in current to the previous current) in the deflection will be (the main current remains the same)
A moving coil galvanometer has 150 equal divisions. Its current sensitivity is 10-divisions per milliampere and voltage sensitivity is 2 divisions per millivolt. In order that each division reads 1 volt, the resistance in ohms needed to be connected in series with the coil will be ______.
How is current sensitivity increased?
