Advertisements
Advertisements
Questions
State how a moving coil galvanometer can be converted into an ammeter.
How will you convert a moving coil galvanometer into an ammeter?
Briefly explain why and how a galvanometer is converted into an ammeter.
Solution 1
- A moving-coil galvanometer is transformed into an ammeter by connecting a low-resistance S across the coil and lowering its effective resistance.
- A shunt is a parallel low resistance that shunts a portion of the current around the coil, as seen in the image below. As a result, the range of currents over which the metre can be used is expanded.
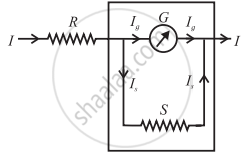
Ammeter - Let I be the maximum current to be measured and Ig be the current for which the galvanometer of resistance G shows a full-scale deflection. Then, the shunt resistance S should be such that the remaining current I - Ig = IS is shunted through it.
- The potential difference across the galvanometer in the parallel combination is equivalent to the potential difference across the shunt.
∴ IgG = IsS = (I - Ig)S
∴ S = `("I"_"g"/("I" - "I"_"g"))"G"`
Solution 2
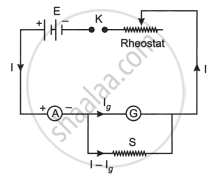
Only small currents may be detected by a galvanometer. Thus, it is transformed into an ammeter to measure enormous currents. By joining a low resistance known as a shunt resistance in parallel with the galvanometer, it can be transformed into an ammeter.
Let S be the low resistance connected in parallel with the galvanometer, G be the resistance of the galvanometer, and I be the maximum current to be measured for full-scale deflection in the galvanometer. Since the galvanometer and shunt resistances are connected in parallel.
∴ The potential difference across 'S' = Potential difference across G
(I - lg)S = lgG
Notes
Students should refer to the answer according to their questions and marks.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The combined resistance of a galvanometer of resistance 500Ω and its shunt is 21Ω. Calculate the value of shunt.
The combined resistance of a galvanometer of resistance 500Ω and its shunt is 21Ω. Calculate the value of shunt.
Write the underlying principle of a moving coil galvanometer.
A circular coil of 250 turns and diameter 18 cm carries a current of 12A. What is the magnitude of magnetic moment associated with the coil?
A galvanometer of resistance G is converted into a voltmeter to measure upto V volts by connecting a resistance R1 in series with the coil. If a resistance R2 is connected in series with it, then it can measures upto V/2 volts. Find the resistance, in terms of R1 and R2, required to be connected to convert it into a voltmeter that can read upto 2 V. Also find the resistance G of the galvanometer in terms of R1 and R2
Two moving coil meters, M1 and M2 have the following particulars:
R1 = 10 Ω, N1 = 30,
A1 = 3.6 × 10–3 m2, B1 = 0.25 T
R2 = 14 Ω, N2 = 42,
A2 = 1.8 × 10–3 m2, B2 = 0.50 T
(The spring constants are identical for the two meters).
Determine the ratio of
- current sensitivity and
- voltage sensitivity of M2 and M1.
Explain how moving coil galvanometer is converted into a voltmeter. Derive the necessary formula.
The fraction of the total current passing through the galvanometer is ............ .
a) `S/(S+G)`
b) `G/(S+G)`
c) `(S+G)/G`
d) `(S+G)/S`
A moving coil galvanometer has a resistance of 25Ω and gives a full scale deflection for a current of 10mA. How will you convert it into a voltmeter having range 0 - 100 V?
A galvanometer has a resistance of 16Ω. It shows full scale deflection, when a current of 20 mA is passed through it. The only shunt resistance available is 0.06 which is not appropriate to convert a galvanometer into an ammeter. How much resistance should be connected in series with the coil of galvanometer, so that the range of ammeter is 8 A?
Why is it necessary to introduce a radial magnetic field inside the coil of a galvanometer?
Can a galvanometer as such be used for measuring the current? Explain.
How will you convert a moving coil galvanometer into a voltmeter?
With the help of a neat and labelled diagram, explain the principle and working of a moving coil galvanometer ?
Define the current sensitivity of a galvanometer ?
Draw a labelled diagram of a moving coil galvanometer and explain its working. What is the function of radial magnetic field inside the coil?
State the principle of the working of a moving coil galvanometer, giving its labeled diagram ?
Outline the necessary steps to convert a galvanometer of resistance RG into an ammeter of a given range ?
State the underlying principle of working of a moving coil galvanometer. Write two reasons why a galvanometer can not be used as such to measure current in a given circuit. Name any two factors on which the current sensitivity of a galvanometer depends.
What are the advantages of using soft iron as a core, instead of steel, in the coils of galvanometers?
A coil of radius 10 cm and resistance 40 Ω has 1000 turns. It is placed with its plane vertical and its axis parallel to the magnetic meridian. The coil is connected to a galvanometer and is rotated about the vertical diameter through an angle of 180°. Find the charge which flows through the galvanometer if the horizontal component of the earth's magnetic field is BH = 3.0 × 10−5 T.
Why are the pole pieces of a horseshoe magnet in a moving coil galvanometer made cylinder in shape?
A moving coil galvanometer has a coil of resistance 59 Ω. It shows a full-scale deflection for a current of 50 mA. How will you convert it to an ammeter having a range of 0 to 3A?
Explain the significance of a radial magnetic field when a current-carrying coil is kept in it.
Define the term 'current sensitivity' of a moving coil galvanometer.
A galvanometer coil has a resistance of 12 Ω and the metre shows full scale deflection for a current of 3 mA. How will you convert the metre into a voltmeter of range 0 to 18 V?
A galvanometer coil has a resistance of 15 Ω and the metre shows full scale deflection for a current of 4 mA. How will you convert the metre into an ammeter of range 0 to 6 A?
The AC voltage across a resistance can be measured using a ______.
The deflection in a moving coil galvanometer is ______.
In a moving coil galvanometer the deflection (Φ) on the scale by a pointer attached to the spring is ______.
The conversion of a moving coil galvanometer into a voltmeter is done by ______.
The coil of a moving coil galvanometer is wound over a metal frame in order to ______.
The current sensitivity of a galvanometer increase by 20%. If its resistance also increases by 25%, the voltage sensitivity will ______.
Assertion (A): On Increasing the current sensitivity of a galvanometer by increasing the number of turns may not necessarily increase its voltage sensitivity.
Reason (R): The resistance of the coil of the galvanometer increases on increasing the number of turns.
Select the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
A galvanometer of resistance 100 Ω gives a full-scale deflection for a current of 10−5 A. To convert it into an ammeter capable of measuring up to 1 A we should connect a resistance of ______.
The coil of galvanometer consists of 100 turns and effective area of 1 square cm. The restoring couple is 10-8 N-m/rad. The magnetic field between the pole pieces is 5T. The current sensitivity of this galvanometer will be ______.
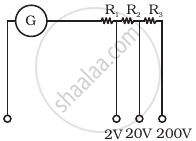
A multirange voltmeter can be constructed by using a galvanometer circuit as shown in figure. We want to construct a voltmeter that can measure 2V, 20V and 200V using a galvanometer of resistance 10Ω and that produces maximum deflection for current of 1 mA. Find R1, R2 and R3 that have to be used.
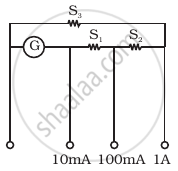
A multirange current meter can be constructed by using a galvanometer circuit as shown in figure. We want a current meter that can measure 10 mA, 100 mA and 1A using a galvanometer of resistance 10 Ω and that prduces maximum deflection for current of 1mA. Find S1, S2 and S3 that have to be used
When a galvanometer is shunted with a 4 Ω resistance, the deflection is reduced to one-fifth. If the galvanometer is further shunted with a 2 Ω wire. The further reduction (find the ratio of decrease in current to the previous current) in the deflection will be (the main current remains the same)
A galvanometer coil bas 500 turns and each tum has an average area of 3 × 10-4 m2. If a torque of 1.5 Nm is required to keep this coil parallel to a magnetic field when a current of 0.5 A is flowing through it, the strength of the field (in T) is ______.
A galvanometer having a resistance of 20 Ω and 30 Ω division on both sides has figure of merit 0.005 ampere/division. The resistance that should be connected in series such that it can be used as a voltmeter upto 15 volt, is ______.
A galvanometer shows full-scale deflection for current Ig. A resistance R1 is required to convert it into a voltmeter of range (0 - V) and a resistance R2 to convert it into a voltmeter of range (0 - 2V). Find the resistance of the galvanometer.
A resistance of 3Ω is connected in parallel to a galvanometer of resistance 297Ω. Find the fraction of current passing through the galvanometer.
A voltmeter has a range of 0 - 20 V and a resistance of 500 Q. Explain how can be used to measure voltages from 0 - 200 volt?
A moving coil galvanometer of resistance 55 Ω produces a full scale deflection for a current of 250 mA. How will you convert it into an ammeter with a range of 0 - 3A?
To convert a moving coil galvanometer into an ammeter we need to connect a ______.
Assertion: When an electric current is passed through a moving coil galvanometer, its coil gets deflected.
Reason: A circular coil produces a uniform magnetic field around itself when an electric current is passed through it.
A galvanometer of resistance 100 Ω gives a full-scale deflection for a potential difference of 200 mV.
- What must be the resistance connected to convert the galvanometer into an ammeter of the range 0-200 mA?
- Determine resistance of the ammeter.
