Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Assertion (A): On Increasing the current sensitivity of a galvanometer by increasing the number of turns may not necessarily increase its voltage sensitivity.
Reason (R): The resistance of the coil of the galvanometer increases on increasing the number of turns.
Select the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
Options
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
A is true but R is false.
A is false and R is also false.
Solution
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Explanation:
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A galvanometer of resistance G is converted into a voltmeter to measure upto V volts by connecting a resistance R1 in series with the coil. If a resistance R2 is connected in series with it, then it can measures upto V/2 volts. Find the resistance, in terms of R1 and R2, required to be connected to convert it into a voltmeter that can read upto 2 V. Also find the resistance G of the galvanometer in terms of R1 and R2
Draw a labelled diagram of a moving coil galvanometer. Describe briefly its principle and working.
- A circular coil of 30 turns and radius 8.0 cm carrying a current of 6.0 A is suspended vertically in a uniform horizontal magnetic field of magnitude 1.0 T. The field lines make an angle of 60° with the normal of the coil. Calculate the magnitude of the counter torque that must be applied to prevent the coil from turning.
- Would your answer change, if the circular coil in (a) were replaced by a planar coil of some irregular shape that encloses the same area? (All other particulars are also unaltered.)
The fraction of the total current passing through the galvanometer is ............ .
a) `S/(S+G)`
b) `G/(S+G)`
c) `(S+G)/G`
d) `(S+G)/S`
Why does a galvanometer when connected in series with a capacitor show a momentary deflection, when it is being charged or discharged?
How does this observation lead to modifying the Ampere's circuital law?
Hence write the generalised expression of Ampere's law.
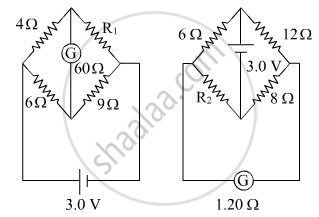
Figure shows two circuits each having a galvanometer and a battery of 3V.
When the galvanometers in each arrangement do not show any deflection, obtain the ratio R1/R2.
The AC voltage across a resistance can be measured using a ______.
The current sensitivity of a galvanometer is defined as ______.
A moving coil galvanometer can be converted into an ammeter by ______.
