Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
How will you convert a moving coil galvanometer into a voltmeter?
Solution
By connecting high resistance in series
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A rectangular coil of a moving coil galvanometer contains 50 turns each having area 12 cm2 . It is suspended in radial magnetic field 0.025 Wb/m2 by a fibre of twist constant 15 x10-10 Nm/degree. Calculate the sensitivity of the moving coil galvanometer.
Increasing the current sensitivity of a galvanometer may not necessarily increase its voltage sensitivity. Explain, giving reason.
Define the current sensitivity of a galvanometer ?
Draw a labelled diagram of a moving coil galvanometer and explain its working. What is the function of radial magnetic field inside the coil?
What are the advantages of using soft iron as a core, instead of steel, in the coils of galvanometers?
A coil of radius 10 cm and resistance 40 Ω has 1000 turns. It is placed with its plane vertical and its axis parallel to the magnetic meridian. The coil is connected to a galvanometer and is rotated about the vertical diameter through an angle of 180°. Find the charge which flows through the galvanometer if the horizontal component of the earth's magnetic field is BH = 3.0 × 10−5 T.
In an ammeter 0.5% of main current passes through galvanometer; If resistance of galvanometer is G, the resistance of ammeter will be.
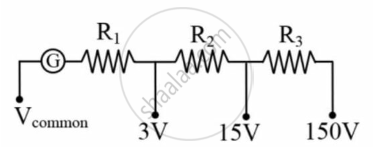
A voltmeter of variable ranges 3 V, 15 V, 150 V is to be designed by connecting resistances R1, R2, R3 in series with a galvanometer of resistance G = 20 Ω, as shown in Fig. The galvanometer gives full pass through its coil for 1 mA current i.e. "gives full pass through it's coil for 1 mA current". Then, the resistances R1, R2 and R3 (in kilo ohms) should be, respectively:
Explain in brief the basic construction of a moving-coil table galvanometer whit a neat labelled diagram.
