Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
When a galvanometer is shunted with a 4 Ω resistance, the deflection is reduced to one-fifth. If the galvanometer is further shunted with a 2 Ω wire. The further reduction (find the ratio of decrease in current to the previous current) in the deflection will be (the main current remains the same)
Options
`(8/13)` of the deflection when shunted with 4 Ω only
`(5/13)` of the deflection when shunted with 4 Ω only
`(3/4)` of the deflection when shunted with 4 Ω only
`(3/13)` of the deflection when shunted with 4 Ω only
MCQ
Solution
`(8/13)` of the deflection when shunted with 4 Ω only.
Explanation:
Case I:
`"Rg"xx1/5 = ("I"-"I"/5)xx4`
⇒ Rg = 16 Ω
Case II:
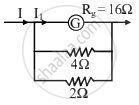
16 I1 = `(4xx2)/6`(I - I1) ⇒ I1 = I/13
So decrease in current to previous current
= `("I"//5-"I"//13)/("I"//5) = 8/13`
shaalaa.com
Is there an error in this question or solution?
