Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A multirange current meter can be constructed by using a galvanometer circuit as shown in figure. We want a current meter that can measure 10 mA, 100 mA and 1A using a galvanometer of resistance 10 Ω and that prduces maximum deflection for current of 1mA. Find S1, S2 and S3 that have to be used
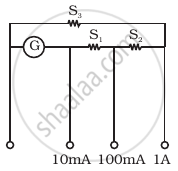
Solution
A galvanometer can be converted into ammeter by connecting a very low resistance wire (shunt S) connected in parallel with galvanometer. The relationship is given by IgG = (I – Ig) S, where Ig is the range of galvanometer and G is the resistance of galvanometer.

For measuring `I_1 = 10 mA: I_G.G = (I_1 - I_G)(S_1 + S_2 + S_3)`
For measuring `I_2 = 100 mA: I_G(G + S_1) = (I_2 - I_G)(S_2 + S_3)`
For measuring `I_3 = 1 A: I_G(G + S_1 + S_2) = (I_3 - I_G)(S_3)`
Gives `S_1 = 1 Ω, S_2 = 0.1 Ω`
And `S_3 = 0.01 Ω`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Show that the current flowing through a moving coil galvanometer is directly proportional to the angle of deflection of coil.
An ideal voltmeter has _______.
(A) low resistance
(b) high resistance
(C) infinite resistance
(D) zero resistance
- A circular coil of 30 turns and radius 8.0 cm carrying a current of 6.0 A is suspended vertically in a uniform horizontal magnetic field of magnitude 1.0 T. The field lines make an angle of 60° with the normal of the coil. Calculate the magnitude of the counter torque that must be applied to prevent the coil from turning.
- Would your answer change, if the circular coil in (a) were replaced by a planar coil of some irregular shape that encloses the same area? (All other particulars are also unaltered.)
Explain how moving coil galvanometer is converted into a voltmeter. Derive the necessary formula.
Can a galvanometer as such be used for measuring the current? Explain.
Draw a labelled diagram of a moving coil galvanometer and explain its working. What is the function of radial magnetic field inside the coil?
Why are the pole pieces of a horseshoe magnet in a moving coil galvanometer made cylinder in shape?
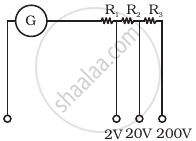
A multirange voltmeter can be constructed by using a galvanometer circuit as shown in figure. We want to construct a voltmeter that can measure 2V, 20V and 200V using a galvanometer of resistance 10Ω and that produces maximum deflection for current of 1 mA. Find R1, R2 and R3 that have to be used.
A moving coil galvanometer of resistance 55 Ω produces a full scale deflection for a current of 250 mA. How will you convert it into an ammeter with a range of 0 - 3A?
