Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
An ideal voltmeter has _______.
(A) low resistance
(b) high resistance
(C) infinite resistance
(D) zero resistance
Solution
(c) Infinite resistance
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The combined resistance of a galvanometer of resistance 500Ω and its shunt is 21Ω. Calculate the value of shunt.
Why does a galvanometer show a momentary deflection at the time of charging or discharging a capacitor? Write the necessary expression to explain this observation.
A circular coil of 250 turns and diameter 18 cm carries a current of 12A. What is the magnitude of magnetic moment associated with the coil?
Draw a labelled diagram of a moving coil galvanometer. Describe briefly its principle and working.
Why is it necessary to introduce a cylindrical soft iron core inside the coil of a galvanometer?
Increasing the current sensitivity of a galvanometer may not necessarily increase its voltage sensitivity. Explain, giving reason.
A rectangular coil of a moving coil galvanometer contains 100 turns, each having area
15 cm2. It is suspended in the radial magnetic field 0.03 T. The twist constant of suspension
fibre is 15 x 10-10 N-m/degree. Calculate the sensitivity of the moving coil galvanometer.
The fraction of the total current passing through the galvanometer is ............ .
a) `S/(S+G)`
b) `G/(S+G)`
c) `(S+G)/G`
d) `(S+G)/S`
A moving coil galvanometer has a resistance of 25Ω and gives a full scale deflection for a current of 10mA. How will you convert it into a voltmeter having range 0 - 100 V?
A galvanometer has a resistance of 16Ω. It shows full scale deflection, when a current of 20 mA is passed through it. The only shunt resistance available is 0.06 which is not appropriate to convert a galvanometer into an ammeter. How much resistance should be connected in series with the coil of galvanometer, so that the range of ammeter is 8 A?
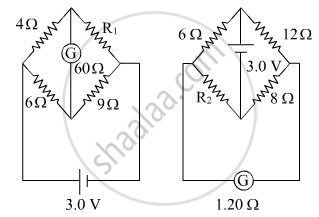
Figure shows two circuits each having a galvanometer and a battery of 3V.
When the galvanometers in each arrangement do not show any deflection, obtain the ratio R1/R2.
Explain, giving reasons, the basic difference in converting a galvanometer into (i) a voltmeter and (ii) an ammeter?
In the meter bridge experiment, balance point was observed at J with AJ = l.
(i) The values of R and X were doubled and then interchanged. What would be the new position of balance point?
(ii) If the galvanometer and battery are interchanged at the balance position, how will the alance point get affected?

State the principle of the working of a moving coil galvanometer, giving its labeled diagram ?
Outline the necessary steps to convert a galvanometer of resistance RG into an ammeter of a given range ?
State the underlying principle of working of a moving coil galvanometer. Write two reasons why a galvanometer can not be used as such to measure current in a given circuit. Name any two factors on which the current sensitivity of a galvanometer depends.
A coil of radius 10 cm and resistance 40 Ω has 1000 turns. It is placed with its plane vertical and its axis parallel to the magnetic meridian. The coil is connected to a galvanometer and is rotated about the vertical diameter through an angle of 180°. Find the charge which flows through the galvanometer if the horizontal component of the earth's magnetic field is BH = 3.0 × 10−5 T.
Why are the pole pieces of a horseshoe magnet in a moving coil galvanometer made cylinder in shape?
A moving coil galvanometer has a coil of resistance 59 Ω. It shows a full-scale deflection for a current of 50 mA. How will you convert it to an ammeter having a range of 0 to 3A?
State how a moving coil galvanometer can be converted into an ammeter.
Define the term 'current sensitivity' of a moving coil galvanometer.
A galvanometer coil has a resistance of 12 Ω and the metre shows full scale deflection for a current of 3 mA. How will you convert the metre into a voltmeter of range 0 to 18 V?
A galvanometer coil has a resistance of 15 Ω and the metre shows full scale deflection for a current of 4 mA. How will you convert the metre into an ammeter of range 0 to 6 A?
The AC voltage across a resistance can be measured using a ______.
The current sensitivity of a galvanometer is defined as ______.
The conversion of a moving coil galvanometer into a voltmeter is done by ______.
The coil of a moving coil galvanometer is wound over a metal frame in order to ______.
The current sensitivity of a galvanometer increase by 20%. If its resistance also increases by 25%, the voltage sensitivity will ______.
A galvanometer of resistance 100 Ω gives a full-scale deflection for a current of 10−5 A. To convert it into an ammeter capable of measuring up to 1 A we should connect a resistance of ______.
A galvanometer having a coil resistance of 60 Ω shows full-scale deflection when a current of 1.0 amp passes through it. It can be converted into an ammeter to read currents up to 5.0 amp by:
In an ammeter 0.5% of main current passes through galvanometer; If resistance of galvanometer is G, the resistance of ammeter will be.
The coil of galvanometer consists of 100 turns and effective area of 1 square cm. The restoring couple is 10-8 N-m/rad. The magnetic field between the pole pieces is 5T. The current sensitivity of this galvanometer will be ______.
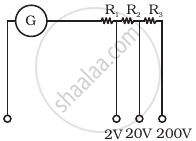
A multirange voltmeter can be constructed by using a galvanometer circuit as shown in figure. We want to construct a voltmeter that can measure 2V, 20V and 200V using a galvanometer of resistance 10Ω and that produces maximum deflection for current of 1 mA. Find R1, R2 and R3 that have to be used.
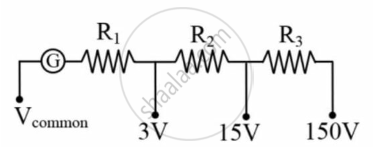
A voltmeter of variable ranges 3 V, 15 V, 150 V is to be designed by connecting resistances R1, R2, R3 in series with a galvanometer of resistance G = 20 Ω, as shown in Fig. The galvanometer gives full pass through its coil for 1 mA current i.e. "gives full pass through it's coil for 1 mA current". Then, the resistances R1, R2 and R3 (in kilo ohms) should be, respectively:
A galvanometer coil bas 500 turns and each tum has an average area of 3 × 10-4 m2. If a torque of 1.5 Nm is required to keep this coil parallel to a magnetic field when a current of 0.5 A is flowing through it, the strength of the field (in T) is ______.
A moving coil galvanometer has 150 equal divisions. Its current sensitivity is 10-divisions per milliampere and voltage sensitivity is 2 divisions per millivolt. In order that each division reads 1 volt, the resistance in ohms needed to be connected in series with the coil will be ______.
A galvanometer shows full-scale deflection for current Ig. A resistance R1 is required to convert it into a voltmeter of range (0 - V) and a resistance R2 to convert it into a voltmeter of range (0 - 2V). Find the resistance of the galvanometer.
How is current sensitivity increased?
Explain in brief the basic construction of a moving-coil table galvanometer whit a neat labelled diagram.
A resistance of 3Ω is connected in parallel to a galvanometer of resistance 297Ω. Find the fraction of current passing through the galvanometer.
A moving coil galvanometer of resistance 55 Ω produces a full scale deflection for a current of 250 mA. How will you convert it into an ammeter with a range of 0 - 3A?
To convert a moving coil galvanometer into an ammeter we need to connect a ______.
Assertion: When an electric current is passed through a moving coil galvanometer, its coil gets deflected.
Reason: A circular coil produces a uniform magnetic field around itself when an electric current is passed through it.
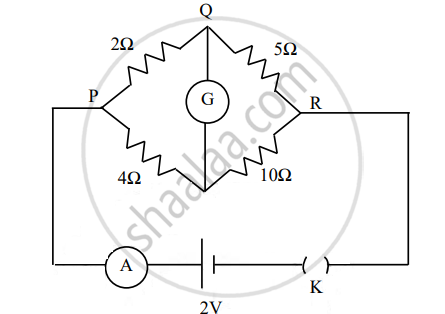
The figure below shows a circuit containing an ammeter A, a galvanometer G and a plug key K. When the key is closed:
A galvanometer of resistance 100 Ω gives a full-scale deflection for a potential difference of 200 mV.
- What must be the resistance connected to convert the galvanometer into an ammeter of the range 0-200 mA?
- Determine resistance of the ammeter.
