Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Why is it necessary to introduce a cylindrical soft iron core inside the coil of a galvanometer?
Solution
The cylindrical soft iron core, when placed inside the coil of a galvanometer, makes the magnetic field stronger and radial in the space between it and pole pieces, such that whatever the position of the rotation of the coil is the magnetic field is always parallel to its plane.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The combined resistance of a galvanometer of resistance 500Ω and its shunt is 21Ω. Calculate the value of shunt.
A circular coil of 250 turns and diameter 18 cm carries a current of 12A. What is the magnitude of magnetic moment associated with the coil?
Two moving coil meters, M1 and M2 have the following particulars:
R1 = 10 Ω, N1 = 30,
A1 = 3.6 × 10–3 m2, B1 = 0.25 T
R2 = 14 Ω, N2 = 42,
A2 = 1.8 × 10–3 m2, B2 = 0.50 T
(The spring constants are identical for the two meters).
Determine the ratio of
- current sensitivity and
- voltage sensitivity of M2 and M1.
Define current sensitivity of a galvanometer.
Why does a galvanometer when connected in series with a capacitor show a momentary deflection, when it is being charged or discharged?
How does this observation lead to modifying the Ampere's circuital law?
Hence write the generalised expression of Ampere's law.
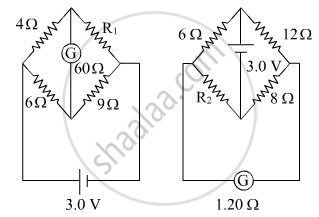
Figure shows two circuits each having a galvanometer and a battery of 3V.
When the galvanometers in each arrangement do not show any deflection, obtain the ratio R1/R2.
A moving coil galvanometer can be converted into an ammeter by ______.
A galvanometer of resistance 100 Ω gives a full-scale deflection for a current of 10−5 A. To convert it into an ammeter capable of measuring up to 1 A we should connect a resistance of ______.
To convert a moving coil galvanometer into an ammeter we need to connect a ______.
