Commerce (English Medium)
Science (English Medium)
Arts (English Medium)
Academic Year: 2013-2014
Date: March 2014
Advertisements
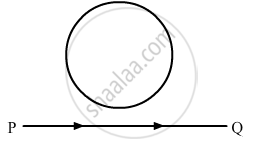
A conducting loop is held above a current carrying wire PQ as shown in the figure. Depict the direction of the current induced in the loop when the current in the wire PQ is constantly increasing.
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
Using the concept of force between two infinitely long parallel current carrying conductors, define one ampere of current.
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
Why is the use of A.C. voltage preferred over D.C. voltage ? Give two reasons.
Chapter: [0.07] Alternating Current
Why do the electrostatic field lines not form closed loops?
Chapter: [0.01] Electric Charges and Fields
A biconvex lens made of a transparent material of refractive index 1.5 is immersed in water of refractive index 1.33. Will the lens behave as a converging or a diverging lens? Give reason.
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
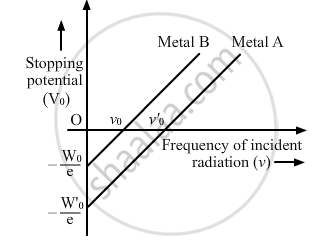
The graph shows the variation of stopping potential with frequency of incident radiation for two photosensitive metals A and B. Which one of the two has higher value of work-function? Justify your answer.
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
To which part of electromagnetic spectrum does a wave of frequency 3 × 1013 Hz belong?
Chapter: [0.08] Electromagnetic Waves
Why is it found experimentally difficult to detect neutrinos in nuclear β-decay?
Chapter: [0.13] Nuclei
Estimate the average drift speed of conduction electrons in a copper wire of cross-sectional area 2.5 × 10−7 m2 carrying a current of 1.8 A. Assume the density of conduction electrons to be 9 × 1028 m−3.
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
Considering the case of a parallel plate capacitor being charged, show how one is required to generalize Ampere's circuital law to include the term due to displacement current.
Chapter: [0.02] Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
Using Rutherford's model of the atom, derive the expression for the total energy of the electron in hydrogen atom. What is the significance of total negative energy possessed by the electron?
Chapter: [0.12] Atoms
Using Bohr's postulates of the atomic model, derive the expression for radius of nth electron orbit. Hence obtain the expression for Bohr's radius.
Chapter: [0.12] Atoms
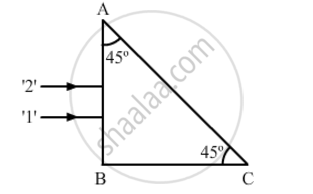
Two monochromatic rays of light are incident normally on the face AB of an isosceles right-angled prism ABC. The refractive indices of the glass prism for the two rays '1' and '2' are respectively 1.3 and 1.5. Trace the path of these rays after entering the prism.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
Write the functions of the following in communication systems:
Transmitter
Chapter: [0.15] Communication Systems
Write the functions of the following in communication systems:
Modulator
Chapter: [0.15] Communication Systems
Advertisements
Show diagrammatically the behaviour of magnetic field lines in the presence of (i) paramagnetic and (ii) diamagnetic substances. How does one explain this distinguishing feature?
Chapter: [0.05] Magnetism and Matter
Draw a circuit diagram of a transistor amplifier in CE configuration.
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Under what condition does the transistor act as an amplifier?
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Draw the circuit diagram of a half wave rectifier and explain its working.
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
A cell of emf 'E' and internal resistance 'r' is connected across a variable resistor 'R'. Plot a graph showing variation of terminal voltage 'V' of the cell versus the current 'I'. Using the plot, show how the emf of the cell and its internal resistance can be determined.
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
A parallel plate capacitor of capacitance C is charged to a potential V. It is then connected to another uncharged capacitor having the same capacitance. Find out the ratio of the energy stored in the combined system to that stored initially in the single capacitor.
Chapter: [0.02] Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
A voltage V = V0 sin ωt is applied to a series LCR circuit. Derive the expression for the average power dissipated over a cycle. Under what condition (i) no power is dissipated even though the current flows through the circuit, (ii) maximum power is dissipated in the circuit?
Chapter: [0.07] Alternating Current
Why are the connections between the resistors in a meter bridge made of thick copper strips?
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
Why is it generally preferred to obtain the balance point in the middle of the meter bridge wire?
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
Which material is used for the meter bridge wire and why?
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
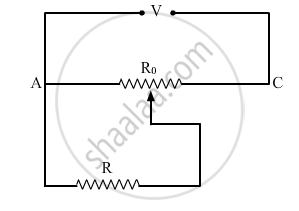
A resistance of R Ω draws current from a potentiometer as shown in the figure. The potentiometer has a total resistance Ro Ω. A voltage V is supplied to the potentiometer. Derive an expression for the voltage across R when the sliding contact is in the middle of the potentiometer.
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
Show, with the help of a diagram, how unpolarised sunlight gets polarised due to scattering.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
Two polaroids P1 and P2 are placed with their pass axes perpendicular to each other. An unpolarised light of intensity Io is incident on P1. A third polaroid P3 is kept in between P1 and P2 such that its pass axis makes an angle of 45° with that of P1. Determine the intensity of light transmitted through P1, P2 and P3
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
Define the term self-inductance of a solenoid.
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
Obtain the expression for the magnetic energy stored in an inductor of self-inductance L to build up a current I through it.
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
For the past some time, Aarti had been observing some erratic body movement, unsteadiness and lack of coordination in the activities of her sister Radha, who also used to complain of severe headache occasionally. Aarti suggested to her parents to get a medical check-up of Radha. The doctor thoroughly examined Radha and diagnosed that she has a brain tumour.
(a) What, according to you, are the values displayed by Aarti?
(b) How can radioisotopes help a doctor to diagnose brain tumour?
Chapter: [0.13] Nuclei
A convex lens of focal length 20 cm is placed coaxially with a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm at a distance of 50 cm apart from each other. A beam of light coming parallel to the principal axis is incident on the convex lens. Find the position of the final image formed by this combination. Draw the ray diagram showing the formation of the image
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Write two basic modes of communication
Chapter: [0.15] Communication Systems
Explain the process of amplitude modulation.
Chapter: [0.15] Communication Systems
Draw a schematic sketch showing how amplitude modulated signal is obtained by superposing a modulating signal over a sinusoidal carrier wave.
Chapter: [0.15] Communication Systems
An electron microscope uses electrons accelerated by a voltage of 50 kV. Determine the de-Broglie wavelength associated with the electrons. Taking other factors, such as numerical aperture etc. to be same, how does the resolving power of an electron microscope compare with that of an optical microscope which used yellow light?
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
Advertisements
Draw the necessary energy band diagrams to distinguish between conductors, semiconductors and insulators.
How does the change in temperature affect the behaviour of these materials ? Explain briefly.
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Deduce an expression for the frequency of revolution of a charged particle in a magnetic field and show that it is independent of velocity or energy of the particle.
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
State the underlying principle of a cyclotron. Write briefly how this machine is used to accelerate charged particles to high energies
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
Draw a labelled diagram of a moving coil galvanometer. Describe briefly its principle and working.
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
Why is it necessary to introduce a cylindrical soft iron core inside the coil of a galvanometer?
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
Increasing the current sensitivity of a galvanometer may not necessarily increase its voltage sensitivity. Explain, giving reason.
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
Draw a labelled diagram of Van de Graaff generator. State its working principle to show how by introducing a small charged sphere into a larger sphere, a large amount of charge can be transferred to the outer sphere. State the use of this machine and also point out its limitations.
Chapter: [0.02] Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
Deduce the expression for the torque acting on a dipole of dipole moment `vecp` in the presence of a uniform electric field `vecE`
Chapter: [0.01] Electric Charges and Fields [0.05] Magnetism and Matter
Consider two hollow concentric spheres, S1 and S2, enclosing charges 2Q and 4Q respectively as shown in the figure. (i) Find out the ratio of the electric flux through them. (ii) How will the electric flux through the sphere S1 change if a medium of dielectric constant 'εr' is introduced in the space inside S1 in place of air ? Deduce the necessary expression
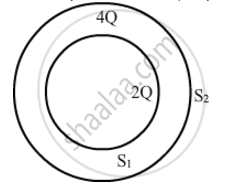
Chapter: [0.01] Electric Charges and Fields
In Young's double slit experiment, describe briefly how bright and dark fringes are obtained on the screen kept in front of a double slit. Hence obtain the expression for the fringe width.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
The ratio of the intensities at minima to the maxima in the Young's double slit experiment is 9 : 25. Find the ratio of the widths of the two slits.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
Describe briefly how a diffraction pattern is obtained on a screen due to a single narrow slit illuminated by a monochromatic source of light. Hence obtain the conditions for the angular width of secondary maxima and secondary minima.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
Two wavelengths of sodium light of 590 nm and 596 nm are used in turn to study the diffraction taking place at a single slit of aperture 2 × 10−6 m. The distance between the slit and the screen is 1·5 m. Calculate the separation between the positions of first maxima of the diffraction pattern obtained in the two cases.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
Other Solutions
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
CBSE previous year question papers Class 12 Physics with solutions 2013 - 2014
Previous year Question paper for CBSE Class 12 Physics-2014 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Physics, you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of CBSE Class 12.
How CBSE Class 12 Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Physics will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.
