Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A moving coil galvanometer of resistance 55 Ω produces a full scale deflection for a current of 250 mA. How will you convert it into an ammeter with a range of 0 - 3A?
Solution
Galvanometer - Ammeter
and shunt is parallel to galvanometer
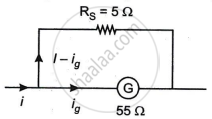
Rs(I - ig) = igG
`"R"_"s" = (250 xx 10^-3 xx 55)/(3 - 250 xx 10^-3)`
`"R"_"s" = 13.75/2.75`
Rs = 5 Ω
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Two moving coil meters, M1 and M2 have the following particulars:
R1 = 10 Ω, N1 = 30,
A1 = 3.6 × 10–3 m2, B1 = 0.25 T
R2 = 14 Ω, N2 = 42,
A2 = 1.8 × 10–3 m2, B2 = 0.50 T
(The spring constants are identical for the two meters).
Determine the ratio of
- current sensitivity and
- voltage sensitivity of M2 and M1.
- A circular coil of 30 turns and radius 8.0 cm carrying a current of 6.0 A is suspended vertically in a uniform horizontal magnetic field of magnitude 1.0 T. The field lines make an angle of 60° with the normal of the coil. Calculate the magnitude of the counter torque that must be applied to prevent the coil from turning.
- Would your answer change, if the circular coil in (a) were replaced by a planar coil of some irregular shape that encloses the same area? (All other particulars are also unaltered.)
Why does a galvanometer when connected in series with a capacitor show a momentary deflection, when it is being charged or discharged?
How does this observation lead to modifying the Ampere's circuital law?
Hence write the generalised expression of Ampere's law.
Explain, giving reasons, the basic difference in converting a galvanometer into (i) a voltmeter and (ii) an ammeter?
In the meter bridge experiment, balance point was observed at J with AJ = l.
(i) The values of R and X were doubled and then interchanged. What would be the new position of balance point?
(ii) If the galvanometer and battery are interchanged at the balance position, how will the alance point get affected?

Define the term 'current sensitivity' of a moving coil galvanometer.
The coil of a moving coil galvanometer is wound over a metal frame in order to ______.
In an ammeter 0.5% of main current passes through galvanometer; If resistance of galvanometer is G, the resistance of ammeter will be.
A moving coil galvanometer has 150 equal divisions. Its current sensitivity is 10-divisions per milliampere and voltage sensitivity is 2 divisions per millivolt. In order that each division reads 1 volt, the resistance in ohms needed to be connected in series with the coil will be ______.
