ISC (Science)
Academic Year: 2022-2023
Date & Time: 6th March 2023, 2:00 pm
Duration: 3h
Advertisements
- Candidates are allowed an additional 10 minutes for only reading the paper.
- They must NOT start writing during this time.
- This question paper is divided into four Sections: A, B, C and D.
- Answer all questions.
- Section A consists of one question having sub-parts of one mark each.
- Section B consists of seven questions of two marks each.
- Section C consists of nine questions of three marks each.
- Section D consists of three questions of five marks each.
- Internal choices have been provided in two questions each in Section B, Section C and Section D.
- The intended marks for questions are given in brackets [].
- All work, including rough work, should be done on the Same sheet as and adjacent to the rest of the answer.
- Answers to sub-parts of the same question must be given in one place only.
- A list of useful physical constants is given at the end of this paper.
- A simple scientific calculator without a programmable memory may be used for calculations.
A hollow sphere of radius R has a point charge Q at its centre. Electric flux emanating from it is `phi`. If both the charge and the radius of the sphere are doubled, electric flux emanating from the sphere will ______.
remain the same
become `2phi`
become `4phi`
become `8phi`
Chapter: [0.011000000000000001] Electric Charges and Fields
An electric current (I) flowing through a metallic wire is gradually increased. The graph of heating power (P) developed in it versus the current (I) is ______.

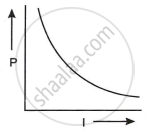
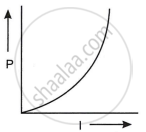
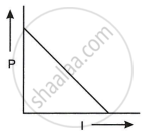
Chapter: [0.02] Current Electricity
A circular coil has radius ‘r', number of turns ‘N’ and carries a current ‘I’. Magnetic flux density ‘B’ at its centre is ______.
B = μ0NI
B = `(μ_0"NI")/"2r"`
B = `(μ_0"NI")/(4πr)`
B = `(μ_0"NI")/"4r"`
Chapter: [0.040999999999999995] Electromagnetic Induction
If an object is placed at a distance of 10 cm in front of a concave mirror of a focal length of 20 cm, the image formed will be ______.
Real and 20 cm in front of the mirror
Real and 6.67 cm in front of the mirror.
Virtual and 20 cm behind the mirror.
Virtual and 6.67 cm behind the mirror.
Chapter: [0.061] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
What type of wavefronts are associated with a source infinity?
Cylindrical wavefronts
Plane wavefronts
Spherical wavefronts
All types of wavefronts
Chapter: [0.062] Wave Optics
Matter waves are ______.
waves associated with moving particles.
waves associated with stationary particles.
waves associated with any charged particles.
waves associated with electrons only.
Chapter: [0.07] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
With an increase in the temperature, the electrical conductivity of a semiconductor ______.
decreases.
increases.
does not change.
first increases and then decreases.
Chapter: [0.09] Electronic Devices
What is meant by an equipotential surface?
Chapter: [0.012] Electrostatic Potential, Potential Energy and Capacitance
For a metallic conductor, what is the relation between current density (J), conductivity (σ) and electric field intensity (E)?
Chapter: [0.02] Current Electricity
What is motional emf? State any two factors on which it depends.
Chapter: [0.040999999999999995] Electromagnetic Induction
What is meant by a microscope in normal use?
Chapter: [0.061] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
In a single slit Fraunhofer diffraction experiment, how does the angular width of the central maximum change when the slit width is Increased?
Chapter: [0.062] Wave Optics
Name the type of nuclear reaction that takes place in the core of the Sun.
Chapter: [0.08199999999999999] Nuclei
What type of semiconductor is obtained when a crystal of silicon is doped with a trivalent element?
Chapter: [0.09] Electronic Devices
Calculate equivalent capacitance of the circuit shown in the Figure given below:
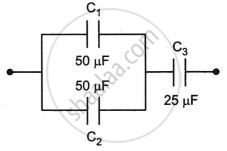
Chapter: [0.012] Electrostatic Potential, Potential Energy and Capacitance
Calculate electric potential at a point P which is at a distance of 9 cm from a point charge of 50 μC.
Chapter: [0.012] Electrostatic Potential, Potential Energy and Capacitance
Write balancing condition of a Wheatstone bridge.
Chapter: [0.02] Current Electricity
Current ‘I’ flowing through a metallic wire is related to drift speed νd of free electrons as follows:
I = nAeνd,
State what the symbol ‘n’ stands for.
Chapter:
Advertisements
When an electric current is passed through a wire or a coil, a magnetic field is produced. Is the reverse phenomenon possible i.e, can a magnetic field produce an electric current? Explain with the help of an appropriate example.
Chapter: [0.040999999999999995] Electromagnetic Induction
A long straight wire AB carries a current of 5A. P is a proton travelling with a velocity of 2 × 106 m/s, parallel to the wire, 0.2 m from it and in a direction opposite to the current, as shown in Figure below. Calculate the force which magnetic field of the current carrying conductor AB exerts on the proton.
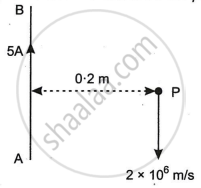
Chapter: [0.031] Moving Charges and Magnetism [0.032] Magnetism and Matter
A moving coil galvanometer of resistance 55 Ω produces a full scale deflection for a current of 250 mA. How will you convert it into an ammeter with a range of 0 - 3A?
Chapter: [0.031] Moving Charges and Magnetism
How are electric vector `(vec "E")`, magnetic vector `(vec "B")` and velocity vector `(vec "C")` oriented in an electromagnetic wave?
Chapter: [0.05] Electromagnetic Waves
Name the electromagnetic wave/radiation which is used to study crystal structure.
Chapter: [0.05] Electromagnetic Waves
Name any two phenomena which take place in the formation of a rainbow.
Chapter: [0.061] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
With reference to semiconductor physics, answer the following question.
What is meant by “Forbidden band" of energy levels?
Chapter: [0.09] Electronic Devices
With reference to semiconductor physics, answer the following question.
In which material “Forbidden band” is absent?
Chapter: [0.09] Electronic Devices
Show that intensity of electric field at a point in broadside position of an electric dipole is given by:
E = `(1/(4piepsilon_0)) "p"/(("r"^2 + l^2)^(3//2))`
Where the terms have their usual meaning.
Chapter: [0.011000000000000001] Electric Charges and Fields
Eight identical cells, each of emf 2V and internal resistance 3 Ω, are connected in series to form a row. Six such rows are connected in parallel to form a battery. This battery is now connected to an external resistor R of resistance 6 Ω. Calculate:
- emf of the battery.
- internal resistance of the battery.
- current flowing through R.
Chapter: [0.02] Current Electricity
In the circuit shown in Figure below, E1 and E2 are batteries having emfs of 25V and 26V. They have an internal resistance of 1 Ω and 5 Ω respectively. Applying Kirchhoff’s laws of electrical networks, calculate the currents I1 and I2.
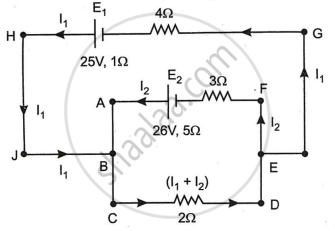
Chapter: [0.02] Current Electricity
Using Ampere’s circuital law, obtain an expression for magnetic flux density ‘B’ at a point near an infinitely long and straight conductor, carrying a current I.
Chapter: [0.031] Moving Charges and Magnetism
Using Huygen's wave theory of light, show that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. Draw a neat and labelled diagram.
Chapter: [0.062] Wave Optics
For any prism, obtain a relation between the angle of the prism (A), the angle of minimum deviation (δm) and the refractive index of its material (μ or n).
Chapter: [0.061] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Obtain an expression for refraction at a single convex spherical surface, i.e., the relation between μ1 (rarer medium), μ2 (denser medium), object distance u, image distance v and the radius of curvature R.
Chapter: [0.061] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
What are the conditions for obtaining a good interference pattern? Give reasons.
Chapter: [0.062] Wave Optics
In Young's double slit experiment, the distance of the 4th bright fringe from the centre of the interference pattern is 1.5 mm. The distance between the slits and the screen is 1.5 m, and the wavelength of light used is 500 nm. Calculate the distance between the two slits.
Chapter: [0.062] Wave Optics
Advertisements
Monochromatic light of wavelength 396 nm is incident on the surface of a metal whose work function is 1.125 eV. Calculate:
- the energy of an incident photon in eV.
- the maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons in eV.
Chapter: [0.062] Wave Optics
Name any two essential parts of a nuclear reactor. State the function of any one of them.
Chapter: [0.08199999999999999] Nuclei
Draw a labelled circuit diagram of a full wave rectifier. Show graphically how the output voltage varies with time.
Chapter: [0.09] Electronic Devices
A 60 Ω resistor, a 1.0 H inductor and a 4 μF capacitor are connected in series to an ac supply generating an emf e = 300 sin (500t) V. Calculate:
- impedance of the circuit.
- peak value of the current flowing through the circuit.
- phase difference between the current and the supply voltage.
Chapter: [0.02] Current Electricity
An ac generator generates an emf which is given by e = 311 sin (240 πt) V. Calculate:
- frequency of the emf.
- r.m.s. value of the emf.
Chapter: [0.02] Current Electricity
The primary coil of a transformer has 60 turns whereas its secondary coil has 3000 turns.
If a 220 V ac voltage is applied to the primary coil, how much emf is induced in the secondary coil?
Chapter: [0.042] Alternating Current
The primary coil of a transformer has 60 turns whereas its secondary coil has 3000 turns.
If a current of 5A flows in the primary coil, how much current will flow in a load in the secondary coil? State the assumption you have made regarding the transformer, in this calculation.
Chapter: [0.042] Alternating Current
Name the series of lines of hydrogen spectrum which lie in the ultraviolet region.
Chapter: [0.081] Atoms
Name the series of lines of hydrogen spectrum which lie in the visible region.
Chapter: [0.081] Atoms
How much is the angular momentum of an electron when it is orbiting in the second Bohr orbit of hydrogen atom?
Chapter: [0.081] Atoms
With reference to Nuclear Physics, answer the following question.
What is meant by Isotopes?
Chapter: [0.08199999999999999] Nuclei
With reference to Nuclear Physics, answer the following question.
Define lu (where u stands for unified atomic mass unit).
Chapter: [0.08199999999999999] Nuclei
Using Bohr’s Theory of hydrogen atom, obtain an expression for the velocity of an electron in the nth orbit of an atom.
Chapter: [0.081] Atoms
What is meant by “binding energy per nucleon” of a nucleus?
Chapter: [0.08199999999999999] Nuclei
State the significance of binding energy per nucleon.
Chapter: [0.08199999999999999] Nuclei
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow.
| There are two types of lenses: Converging lenses and diverging lenses, depending on whether they converge or diverge an incident beam of light. They are also called convex or concave lenses. Lenses are usually made of glass. Convex lenses are more popular as they form a real image of an object. They are widely used in our daily life, for instance, in microscopes, telescopes, projectors, cameras, spectacles, etc. Microscopes are used to view small and nearby objects, whereas telescopes are used to see distant objects. |
- State any one factor on which the focal length of a lens depends.
- Give an example where a convex lens behaves like a diverging lens.
- What type of lens is used in a camera?
- Write an expression for magnifying power of a compound microscope when its final image lies at the least distance of distinct vision (D).
- State any one difference between a reflecting telescope and a refracting telescope.
Chapter:
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
CISCE previous year question papers ISC Class 12 Physics (Theory) with solutions 2022 - 2023
Previous year Question paper for CISCE ISC Class 12 -2023 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Physics (Theory), you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of CISCE ISC Class 12.
How CISCE ISC Class 12 Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Physics (Theory) will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.
