Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Obtain an expression for refraction at a single convex spherical surface, i.e., the relation between μ1 (rarer medium), μ2 (denser medium), object distance u, image distance v and the radius of curvature R.
Solution
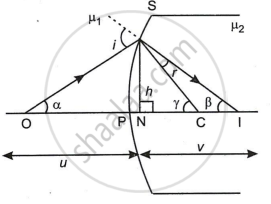
In ΔCOA,
i = α + γ and r = γ - β
γ = r + β
Let O be a point object in the rarer-medium of refractive index μ1 and lying on the principle axis. The image of this object, O is formed by refraction at the convex spherical surface of radius at the point 'I' into the medium 'B' of refractive index μ2 of curvature, as shown in the figure.
The convex surface has a small aperture and the angles of incidence ‘i’ and refraction ‘r’ are small.
Let ∠AOP = α, ∠AIP = β, ∠ACP = γ from A, and draw AN ⊥er to the principle axis for refraction at point A1. By snell's law,
`(sin i)/(sin r) = mu_2/mu_1`
∵ i and r are small.
then `i/r = mu_2/mu_1`
`=> mu_1i = mu_2r`
Substituting the value of i and r.
μ1(α + γ) = μ2(γ - β)
∵ α, β, γ are small, they can be replaced.
∴ μ1(tan α + tan γ) = μ2(tan γ - tan β)
or `mu_1 ("AN"/"NO" + "AN"/"NC") = mu_2 ("AN"/"NC" + "AN"/"NI")`
or `mu_1/"NO" + mu_1/"NC" = mu_2/"NC" - mu_2/"NI"`
Due to small aperture, the point N lies close to P. Also, applying sign convention, we get
NO ~ PO = - u, NC ~ PC = R
NI ~ PI = v
Putting the value in the above expression
`mu_1/(- u) + mu_1/"R" = mu_2/"R" - mu_2/v`
OR
`mu_2/v - mu_1/u = (mu_2 - mu_1)/"R"`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What type of wavefront will emerge from a (i) point source, and (ii) distance light source?
A point source of light is placed at a distance of 2 f from a converging lens of focal length f. The intensity on the other side of the lens is maximum at a distance
A convex lens has a focal length of 10 cm. Find the location and nature of the image if a point object is placed on the principal axis at a distance of (a) 9.8 cm, (b) 10.2 cm from the lens.
A converging lens of focal length 15 cm and a converging mirror of focal length 10 cm are placed 50 cm apart with common principal axis. A point source is placed in between the lens and the mirror at a distance of 40 cm from the lens. Find the locations of the two images formed.
A converging lens of focal length 15 cm and a converging mirror of focal length 10 cm are placed 50 cm apart. If a pin of length 2.0 cm is placed 30 cm from the lens farther away from the mirror, where will the final image form and what will be the size of the final image?
A point object is placed at a distance of 15 cm from a convex lens. The image is formed on the other side at a distance of 30 cm from the lens. When a concave lens is placed in contact with the convex lens, the image shifts away further by 30 cm. Calculate the focal lengths of the two lenses.
According to new Cartesian sign conventions, all the distances are measured from the ______.
Region I and II are separated by a spherical surface of a radius of 25 cm. An object is kept in the region I at a distance of 40 cm from the surface. The distance of the image from the surface is ______.
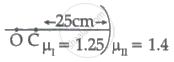
Define the critical angle for a given pair of media and total internal reflection. Obtain the relation between the critical angle and refractive index of the medium.
A point object in the air is placed symmetrically at a distance of 60 cm in front of a concave spherical surface with a refractive index of 1.5. If the radius of curvature of the surface is 20 cm, find the position of the image formed.
