Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Outline the necessary steps to convert a galvanometer of resistance RG into an ammeter of a given range ?
Solution
Conversion of a galvanometer to ammeter
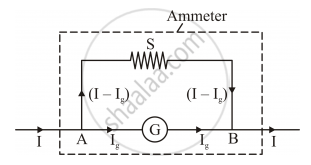
• A shunt (low resistance) is connected in parallel with the galvanometer.
`S = ((I_g)/(I -I_g))G`
Where,
I → Total current in circuit
G → Resistance of the galvanometer
S →Resistance of the shunt
Ig → Current through galvanometer
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The combined resistance of a galvanometer of resistance 500Ω and its shunt is 21Ω. Calculate the value of shunt.
Write the underlying principle of a moving coil galvanometer.
An ideal voltmeter has _______.
(A) low resistance
(b) high resistance
(C) infinite resistance
(D) zero resistance
Two moving coil meters, M1 and M2 have the following particulars:
R1 = 10 Ω, N1 = 30,
A1 = 3.6 × 10–3 m2, B1 = 0.25 T
R2 = 14 Ω, N2 = 42,
A2 = 1.8 × 10–3 m2, B2 = 0.50 T
(The spring constants are identical for the two meters).
Determine the ratio of
- current sensitivity and
- voltage sensitivity of M2 and M1.
Define current sensitivity of a galvanometer.
The current sensitivity of a galvanometer is defined as ______.
The coil of a moving coil galvanometer is wound over a metal frame in order to ______.
The coil of galvanometer consists of 100 turns and effective area of 1 square cm. The restoring couple is 10-8 N-m/rad. The magnetic field between the pole pieces is 5T. The current sensitivity of this galvanometer will be ______.
A galvanometer shows full-scale deflection for current Ig. A resistance R1 is required to convert it into a voltmeter of range (0 - V) and a resistance R2 to convert it into a voltmeter of range (0 - 2V). Find the resistance of the galvanometer.
A moving coil galvanometer of resistance 55 Ω produces a full scale deflection for a current of 250 mA. How will you convert it into an ammeter with a range of 0 - 3A?
