Science (English Medium)
Academic Year: 2010-2011
Date: March 2011
Advertisements
A hollow metal sphere of radius 10 cm is charged such that the potential on its surface is 5 V. What is the potential at the centre of the sphere?
Chapter: [0.02] Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
How are X-rays produced?
Chapter: [0.08] Electromagnetic Waves
Define electric dipole moment. Write its S.I. unit.
Chapter: [0.01] Electric Charges and Fields
Where on the surface of Earth is the angle of dip zero?
Chapter: [0.05] Magnetism and Matter
Define the term ‘stopping potential’ in relation to photo-electric effect.
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
Two bar magnets are quickly moved towards a metallic loop connected across a capacitor ‘C’ as shown in the figure. Predict the polarity of the capacitor.
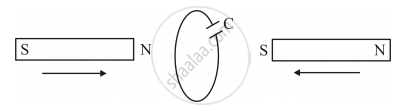
Chapter: [0.01] Electric Charges and Fields
Write any two characteristic properties of nuclear force.
Chapter: [0.13] Nuclei
What happens to the width of depletion player of a p-n junction when it is (i) forward biased, (ii) reverse biased?
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Net capacitance of three identical capacitors in series is 2 μF. What will be their net capacitance if connected in parallel?
Chapter: [0.02] Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
Find the ratio of energy stored in the two configurations if they are both connected to the same source.
Chapter: [0.02] Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
In the meter bridge experiment, balance point was observed at J with AJ = l.
(i) The values of R and X were doubled and then interchanged. What would be the new position of balance point?
(ii) If the galvanometer and battery are interchanged at the balance position, how will the alance point get affected?

Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
Write the expression for Lorentz magnetic force on a particle of charge ‘q’ moving with velocity `vecv` in a magnetic field`vecB`. Show that no work is done by this force on the charged particle.
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
A steady current (I1) flows through a long straight wire. Another wire carrying steady current (I2) in the same direction is kept close and parallel to the first wire. Show with the help of a diagram how the magnetic field due to the current I1 exerts a magnetic force on the second wire. Write the expression for this force.
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
State the principle of working of a transformer. Can a transformer be used to step up or step down a d.c. voltage? Justify your answer.
Chapter: [0.07] Alternating Current
Using the curve for the binding energy per nucleon as a function of mass number A, state clearly how the release in energy in the processes of nuclear fission and nuclear fusion can be explained.
Chapter: [0.13] Nuclei
In the given circuit, assuming point A to be at zero potential, use Kirchhoff’s rules to determine the potential at point B.

Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
Plot a graph showing the variation of coulomb force (F) versus ,`(1/r^2)` where r is the distance between the two charges of each pair of charges: (1 μC, 2 μC) and (2 μC, − 3 μC). Interpret the graphs obtained.
Chapter: [0.01] Electric Charges and Fields
Advertisements
A parallel plate capacitor is being charged by a time varying current. Explain briefly how Ampere’s circuital law is generalized to incorporate the effect due to the displacement current ?
Chapter: [0.02] Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
What is ground wave communication? On what factors does the maximum range of propagation in this mode depend?
Chapter: [0.15] Communication Systems
A thin straight infinitely long conducting wire having charge density λ is enclosed by a cylindrical surface of radius r and length l, its axis coinciding with the length of the wire. Find the expression for the electric flux through the surface of the cylinder.
Chapter: [0.01] Electric Charges and Fields
A compound microscope uses an objective lens of focal length 4 cm and eyepiece lens of focal length 10 cm. An object is placed at 6 cm from the objective lens. Calculate the magnifying power of the compound microscope. Also calculate the length of the microscope.
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
A giant refracting telescope at an observatory has an objective lens of focal length 15 m. If an eyepiece lens of focal length 1.0 cm is used, find the angular magnification of the telescope. If this telescope is used to view the moon, what is the diameter of the image of the moon formed by the objective lens? The diameter of the moon is 3.42 × 106 m and the radius of the lunar orbit is 3.8 × 108 m.
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Using de Broglie’s hypothesis, explain with the help of a suitable diagram, Bohr’s second postulate of quantization of energy levels in a hydrogen atom.
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
The ground state energy of hydrogen atom is −13.6 eV. What are the kinetic and potential energies of the electron in this state?
Chapter: [0.12] Atoms
You are given a circuit below. Write its truth table. Hence, identify the logic operation carried out by this circuit. Draw the logic symbol of the gate it corresponds to.

Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
A convex lens made up of glass of refractive index 1.5 is dipped, in turn, in (i) a medium of refractive index 1.6, (ii) a medium of refractive index 1.3.
(a) Will it behave as a converging or a diverging lens in the two cases?
(b) How will its focal length change in the two media?
Chapter:
Write briefly any two factors which demonstrate the need for modulating a signal. Draw a suitable diagram to show amplitude modulation using a sinusoidal signal as the modulating signal.
Chapter: [0.15] Communication Systems
Draw a labeled diagram of a full wave rectifier circuit. State its working principle. Show the input-output waveforms ?
Chapter: [0.07] Alternating Current
Two heating elements of resistances R1 and R2 when operated at a constant supply of voltage, V, consume powers P1 and P2 respectively. Deduce the expressions for the power of their combination whey they are, in turn, connected in (i) series and (ii) parallel across the same voltage supply.
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
Use the mirror equation to show that an object placed between f and 2f of a concave mirror produces a real image beyond 2f.
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Use the mirror equation to show a convex mirror always produces a virtual image independent of the location of the object ?
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Use the mirror equation to deduce that an object placed between the pole and focus of a concave mirror produces a virtual and enlarged image.
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Draw a plot showing the variation of photoelectric current with collector plate potential for two different frequencies, v1 > v2, of incident radiation having the same intensity. In which case will the stopping potential be higher? Justify your answer.
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
Advertisements
State the working of a.c. generator with the help of a labeled diagram.
The coil of an a.c. generator having N turns, each of area A, is rotated with a constant angular velocity ω. Deduce the expression for the alternating e.m.f. generated in the coil.
What is the source of energy generation in this device?
Chapter: [0.06] Electromagnetic Induction
Show that in an a.c. circuit containing a pure inductor, the voltage is ahead of current by π/2 in phase ?
Chapter: [0.07] Alternating Current
A horizontal straight wire of length L extending from east to west is falling with speed v at right angles to the horizontal component of Earth’s magnetic field B.
(i) Write the expression for the instantaneous value of the e.m.f. induced in the wire.
(ii) What is the direction of the e.m.f.?
(iii) Which end of the wire is at the higher potential?
Chapter: [0.05] Magnetism and Matter
State the importance of coherent sources in the phenomenon of interference.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
In Young’s double slit experiment to produce interference pattern, obtain the conditions for constructive and destructive interference. Hence deduce the expression for the fringe width.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
How does the fringe width get affected, if the entire experimental apparatus of Young is immersed in water?
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
State Huygen’s principle. Using this principle explain how a diffraction pattern is obtained on a screen due to a narrow slit on which a narrow beam coming from a `=> n = (vlamda)/(vlamda_omega)`monochromatic source of light is incident normally.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
Show that the angular width of the first diffraction fringe is half that of the central fringe.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
If a monochromatic source of light is replaced by white light, what change would you observe in the diffraction pattern?
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
State the principle of the working of a moving coil galvanometer, giving its labeled diagram ?
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
Increasing the current sensitivity of a galvanometer may not necessarily increase its voltage sensitivity. Explain, giving reason.
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
Outline the necessary steps to convert a galvanometer of resistance RG into an ammeter of a given range ?
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
Using Ampere’s circuital law, obtain the expression for the magnetic field due to a long solenoid at a point inside the solenoid on its axis ?
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
In what respect is a toroid different from a solenoid?
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
Draw and compare the pattern of the magnetic field lines in the two cases ?
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
How is the magnetic field inside a given solenoid made strong?
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
Other Solutions
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
CBSE previous year question papers Class 12 Physics with solutions 2010 - 2011
Previous year Question paper for CBSE Class 12 Physics-2011 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Physics, you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of CBSE Class 12.
How CBSE Class 12 Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Physics will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.
