Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A parallel plate capacitor is being charged by a time varying current. Explain briefly how Ampere’s circuital law is generalized to incorporate the effect due to the displacement current ?
Solution
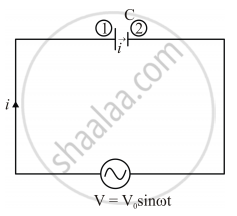
When a capacitor is connected to an alternating current, it offers a resistance `X_e (1/(omegac))`and allows the current to pass through.
As the current is moving from plate (1) to plate (2) there should be a magnetic field associated with this current as explained by Ampere circuital law, but as there can’t be movement of actual electrons from plate (2) to plate (1), there will be no physical current, and still there will be a magnetic field.
To solve this paradox Maxwell altered the form of Ampere’s law as followed.
Original form
`int_c vecE*vecdl =mu_0i +mu_0 in_0 (dphi)/(dt)`
`=mu_0 (i +i_D)`
`i_D = in_0 (dphi_(E))/(dt)`(Displacement current)
`phi_E` = Electric flux
By introducing displacement current, Maxwell argued that due to change in electric field associated with alternating voltage, there will be a time dependent electric flux. This flux will cause a displacement current and hence there will be a magnetic field.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A parallel plate capacitor with air between the plates has a capacitance of 8 pF (1pF = 10−12 F). What will be the capacitance if the distance between the plates is reduced by half, and the space between them is filled with a substance of dielectric constant 6?
A capacitor, made of two parallel plates each of plate area A and separation d, is being charged by an external ac source. Show that the displacement current inside the capacitor is the same as the current charging the capacitor.
A parallel plate air capacitor has a capacitance of 5 μF. It becomes 50 μF when a dielectric medium occupies the entire space between its two plates. What is the dielectric constant of the medium?
A parallel plate capacitor is charged and then disconnected from the charging battery. If the plates are now moved farther apart by pulling them by means of insulating handles, then ______.
Capacitor plates are charged by a battery with ‘V’ volts. After charging the battery is disconnected and a dielectric slab with dielectric constant ‘K’ is inserted between its plates, the potential across the plates of a capacitor will become ____________.
When air replace by dielectric medium of constant K, the maximum force of attraction between two charges separate by a distance.
In a capacitor of capacitance 20 µF the distance between the plates is 5 mm. If a dielectric slab of width 2 mm and dielectric constant 3 is inserted between the plates, then the new capacitor will be ______.
A parallel plate air capacity 'C' farad, potential 'V' volt and energy 'E' joule. When the gap between the plates is completely filled with dielectric ______.
