Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
What happens to the width of depletion player of a p-n junction when it is (i) forward biased, (ii) reverse biased?
Solution
(i) In forward bias, the width of the depletion layer decreases.
(ii) In reverse bias, the width of the depletion layer increases.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Why is zener diode fabricated by heavily doping both p- and n-sides of the junction?
Describe briefly, with the help of a diagram, the role of the two important processes involved in the formation of a p-n junction ?
Explain the formation of depletion layer and potential barrier in a p−n junction.
Answer the following question.
Draw solar cell V-I characteristics.
For LED's to emit light in visible region of electromagnetic light, it should have energy band gap in the range of:
Which one of the following is not the advantage of LED?
The amplifiers X, Y and Z are connected in series. If the voltage gains of X, Y and Z are 10, 20 and 30, respectively and the input signal is 1 mV peak value, then what is the output signal voltage (peak value)
- if dc supply voltage is 10V?
- if dc supply voltage is 5V?
Read the following paragraph and answer the questions.
|
LED is a heavily doped P-N junction which under forward bias emits spontaneous radiation. When it is forward-biased, due to recombination of holes and electrons at the junction, energy is released in the form of photons. In the case of Si and Ge diode, the energy released in recombination lies in the infrared region. LEDs that can emit red, yellow, orange, green and blue light are commercially available. The semiconductor used for fabrication of visible LEDs must at least have a band gap of 1.8 eV. The compound semiconductor Gallium Arsenide – Phosphide is used for making LEDs of different colours.
|
- Why are LEDs made of compound semiconductor and not of elemental semiconductors?
- What should be the order of bandgap of an LED, if it is required to emit light in the visible range?
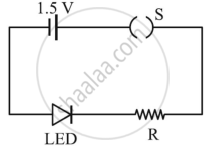
- A student connects the blue coloured LED as shown in the figure. The LED did not glow when switch S is closed. Explain why?
OR
iii. Draw V-I characteristic of a p-n junction diode in
(i) forward bias and (ii) reverse bias
Draw solar cells of I-V characteristics.
How can a photodiode be used to measure light intensity?

