Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Describe briefly, with the help of a diagram, the role of the two important processes involved in the formation of a p-n junction ?
Solution
Two important process involved in the formation of a p-n junction are:
Diffusion and,
Drift
In n-type semiconductor electrons are the majority carriers and holes are minority carriers. In the same way, in p-type semiconductor holes are majority and electrons are minority carriers. During the formation of p-n junction, due to concentration gradient across p- and n-side, holes diffuses from p-side to n-side and electrons diffuses from n-side to p-side. This motion gives rise to diffusion current across the junction.
When an electron diffuses from n- to p-side, it leaves behind a positive charge. In such a manner a positively charged layer forms on n-side of the junction.
Similarly, when a hole diffuses from p- to n-side, it leaves behind a negative charge and a negatively charged layer forms on p-side of the junction.
This space-charge region is known as depletion legion. An electric field directed from positive charge towards negative charge develops. Due to this field, electrons on p-side of the junction move to n-side and holes on n-side of the junction move to p-side. This motion of charge carriers due to the electric field is called drift.
Drift current is opposite in direction to the diffusion current.
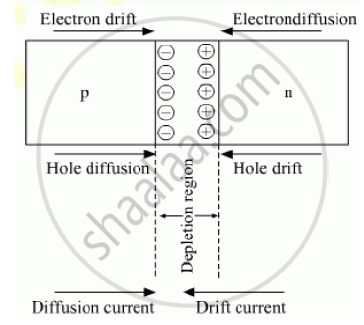
Initially, diffusion current is large and drift current is small. Space-charge region on either side increases as the diffusion process continues. This increases the electric field and hence the drift current. This process continues until the diffusion current equals the drift current. Thus a p-n junction is formed.
RELATED QUESTIONS
How is a Zener diode fabricated?
Explain with the help of a diagram, how depletion region and potential barrier are formed in a junction diode.
With what considerations in view, a photodiode is fabricated? State its working with the help of a suitable diagram.
Even though the current in the forward bias is known to be more than in the reverse bias, yet the photodiode works in reverse bias. What is the reason?
Carbon, silicon and germanium have four valence electrons each. These are characterised by valence and conduction bands separated by energy band gap respectively equal to (Eg)C, (Eg)Si and (Eg)Ge. Which of the following statements is true?
The width of depletion region of p-n junction diode is _______.
(A) 0.5 nm to 1 nm
(B) 5 nm to 10 nm
(C) 50 nm to 500 nm
(D) 500 nm to 1000 nm
Why is zener diode fabricated by heavily doping both p- and n-sides of the junction?
How is a photodiode fabricated?
How does a light emitting diode (LED) work? Give two advantages of LED’s over the conventional incandescent lamps.
Explain how a potential barrier is developed in a p-n junction diode.
Answer the following question.
Explain the three processes involved in solar cell working.
