Science (English Medium)
Academic Year: 2011-2012
Date: March 2012
Advertisements
Two wires of equal length, one of copper and the other of manganin have the same resistance. Which wire is thicker?
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
What are the directions of electric and magnetic field vectors relative to each other and relative to the direction of propagation of electromagnetic waves?
Chapter: [0.08] Electromagnetic Waves
How does the angular separation between fringes in single-slit diffraction experiment change when the distance of separation between the slit screens is doubled?
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
A bar magnet is moved in the direction indicated by the arrow between two coils PQ and CD. Predict the directions of induced current in each coil.
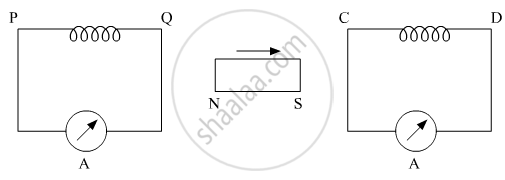
Chapter: [0.06] Electromagnetic Induction
For the same value of angle of incidence, the angles of refraction in three media A, B and C are 15°, 25° and 35° respectively. In which medium would the velocity of light be minimum?
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
A proton and an electron have same kinetic. Which one has greater de-Broglie wavelength and why?
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
Mention the two characteristic properties of the material suitable for making core of a transformer.
Chapter: [0.07] Alternating Current
A charge ‘q’ is placed at the centre of a cube of side l. What is the electric flux passing through each face of the cube?
Chapter: [0.01] Electric Charges and Fields
A test charge ‘q’ is moved without acceleration from A to C along the path from A to B and then from B to C in electric field E as shown in the figure. (i) Calculate the potential difference between A and C. (ii) At which point (of the two) is the electric potential more and why?
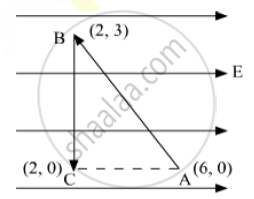
Chapter: [0.02] Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
An electric dipole is held in a uniform electric field.
(i) Show that the net force acting on it is zero.
(ii) The dipole is aligned parallel to the field. Find the work done in rotating it through the angle of 180°.
Chapter: [0.02] Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
State the underlying principle of a transformer. How is the large scale transmission of electric energy over long distances done with the use of transformers?
Chapter: [0.07] Alternating Current
A capacitor of capacitance ‘C’ is being charged by connecting it across a dc source along with an ammeter. Will the ammeter show a momentary deflection during the process of charging? If so, how would you explain this momentary deflection and the resulting continuity of current in the circuit? Write the expression for the current inside the capacitor.
Chapter: [0.02] Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
An object AB is kept in front of a concave mirror as shown in the figure.
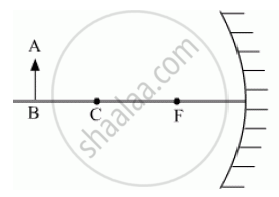
(i) Complete the ray diagram showing the image formation of the object.
(ii) How will the position and intensity of the image be affected if the lower half of the mirror’s reflecting surface is painted black?
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Draw a labeled ray diagram of a reflecting telescope. Mention its two advantages over the refracting telescope.
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Describe briefly with the help of a circuit diagram, how the flow of current carriers in a p-n-p transistor is regulated with emitter-base junction forward biased and base-collector junction reverse biased.
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
In the given block diagram of a receiver, identify the boxes labeled as X and Y and write their functions.
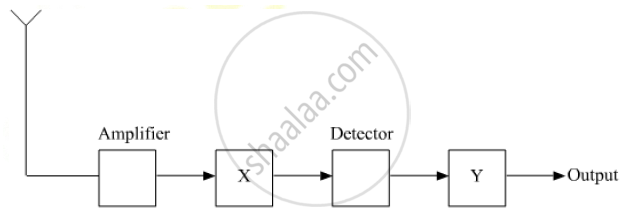
Chapter: [0.15] Communication Systems
Advertisements
A light bulb is rated 100 W for 220 V ac supply of 50 Hz. Calculate
(i) The resistance of the bulb;
(ii) The rms current through the bulb.
Chapter: [0.07] Alternating Current
An alternative voltage given by V = 140 sin 314t is connected across a pure resistor of 50 Ω. Find
- The frequency of the source.
- The rms current is through the resistor.
Chapter: [0.07] Alternating Current
A circular coil of N turns and radius R carries a current I. It is unwound and rewound to make another coil of radius R/2, current I remaining the same. Calculate the ratio of the magnetic moments of the new coil and original coil.
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
Deduce the expression for the electrostatic energy stored in a capacitor of capacitance 'C' and having charge 'Q'.
Chapter: [0.02] Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
How will the (i) energy stored and (ii) the electric field inside the capacitor be affected when it is completely filled with a dielectric material of dielectric constant K?
Chapter: [0.02] Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
Calculate the value of the resistance R in the circuit shown in the figure so that the current in the circuit is 0.2 A. What would b the potential difference between points B and E?
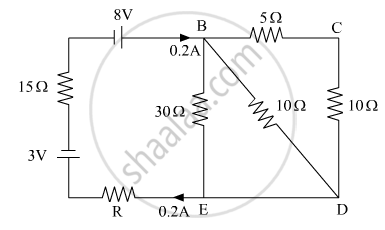
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
You are given three lenses L1, L2 and L3 each of focal length 20 cm. A object is kept at 40 cm in front of L1, as shown. The final real image is formed at the focus ‘I’ of L3. Find the separation between L1, L2 and L3.
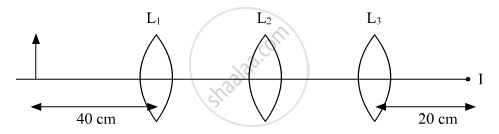
Chapter:
Define the terms (i) ‘cut-off voltage’ and (ii) ‘threshold frequency’ in relation to the phenomenon of photoelectric effect.
Using Einstein’s photoelectric equation shows how the cut-off voltage and threshold frequency for a given photosensitive material can be determined with the help of a suitable plot/graph.
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
A series LCR circuit is connected to an ac source. Using the phasor diagram, derive the expression for the impedance of the circuit. Plot a graph to show the variation of current with frequency of the source, explaining the nature of its variation.
Chapter: [0.07] Alternating Current
Mention three different modes of propagation used in communication system.
Chapter: [0.15] Communication Systems
Explain with the help of a diagram how long distance communication can be achieved by ionospheric reflection of radio waves.
Chapter: [0.15] Communication Systems
Draw a plot of potential energy of a pair of nucleons as a function of their separations. Mark the regions where the nuclear force is (i) attractive and (ii) repulsive.
Chapter: [0.13] Nuclei
Write any two characteristic features of nuclear forces ?
Chapter: [0.13] Nuclei
In a Geiger-Marsden experiment, calculate the distance of closest approach to the nucleus of Z = 80, when a α-particle of 8Mev energy impinges on it before it comes momentarily to rest and reverses its direction.
How will the distance of closest approach be affected when the kinetic energy of the α-particle is doubles?
Chapter: [0.12] Atoms
The ground state energy of hydrogen atom is −13.6 eV. If and electron make a transition from the energy level −0.85 eV to −3.4 eV, calculate spectrum does his wavelength belong?
Chapter: [0.12] Atoms
Define relaxation time of the free electrons drifting in a conductor. How is it related to the drift velocity of free electrons? Use this relation to deduce the expression for the electrical resistivity of the material.
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
In Young's double slit experiment, derive the condition for
(i) constructive interference and
(ii) destructive interference at a point on the screen.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
Advertisements
A beam of light consisting of two wavelengths, 800 nm and 600 nm is used to obtain the interference fringes in a Young's double slit experiment on a screen placed 1 · 4 m away. If the two slits are separated by 0·28 mm, calculate the least distance from the central bright maximum where the bright fringes of the two wavelengths coincide.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
How does an unpolarized light incident on a polaroid get polarized? Describe briefly, with the help of a necessary diagram, the polarization of light by reflection from a transparent medium.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
Two polaroids ‘A’ and ‘B’ are kept in crossed position. How should a third polaroid ‘C’ be placed between them so that the intensity of polarized light transmitted by polaroid B reduces to 1/8th of the intensity of unpolarized light incident on A?
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
Describe briefly, with the help of a diagram, the role of the two important processes involved in the formation of a p-n junction ?
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Name the device which is used as a voltage regulator. Draw the necessary circuit diagram and explain its working?
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Explain briefly the principle on which a transistor-amplifier works as an oscillator. Draw the necessary circuit diagram and explain its working ?
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Identify the equivalent gate for the following circuit and write its truth table.
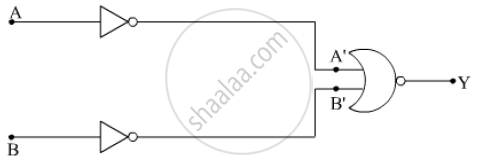
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Write the expression for the force,`vecF` acting on a charged particle of charge ‘q’, moving with a velocity `vecV` in the presence of both electric field `vecF`and magnetic field `vecB` . Obtain the condition under which the particle moves undeflected through the fields.
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
A rectangular loop of size l × b carrying a steady current I is placed in a uniform magnetic field `vecB`. Prove that the torque `vectau`acting on the loop is give by `vectau =vecm xx vecB,`where `vecm` is the magnetic moment of the loop.
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
Explain, giving reasons, the basic difference in converting a galvanometer into (i) a voltmeter and (ii) an ammeter?
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
Two long straight parallel conductors carrying steady currents I1 and I2 are separated by a distance 'd'. Explain briefly, with the help of a suitable diagram, how the magnetic field due to one conductor acts on the other. Hence deduce the expression for the force acting between the two conductors. Mention the nature of this force.
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
Other Solutions
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
CBSE previous year question papers Class 12 Physics with solutions 2011 - 2012
Previous year Question paper for CBSE Class 12 Physics-2012 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Physics, you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of CBSE Class 12.
How CBSE Class 12 Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Physics will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.
